Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism (HH), also known as primary or peripheral/gonadal hypogonadism, is a condition which is characterized by hypogonadism due to an impaired response of the gonads to the gonadotropins, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), and in turn a lack of sex steroid production and elevated gonadotropin levels (as an attempt of compensation by the body). HH may present as either congenital or acquired, but the majority of cases are of the former nature.[1][2]
There are a multitude of different etiologies of HH. Congenital causes include the following:[1][3][4]
Acquired causes (due to damage to or dysfunction of the gonads) include gonadal torsion, vanishing/anorchia, orchitis, premature ovarian failure, ovarian resistance syndrome, trauma, surgery, autoimmunity, chemotherapy, radiation, infections (e.g., sexually-transmitted diseases), toxins (e.g., endocrine disruptors), and drugs (e.g., antiandrogens, opioids, alcohol).[1][3][4]
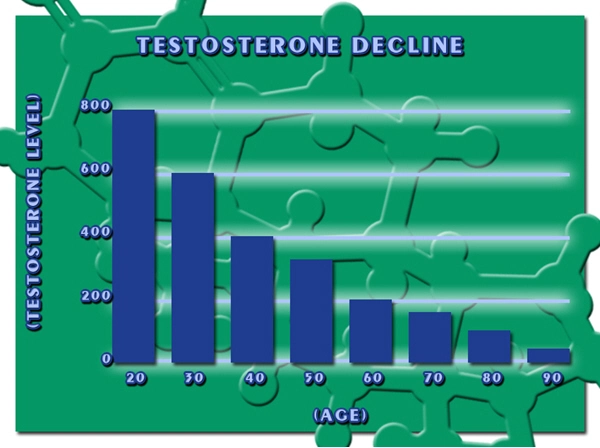
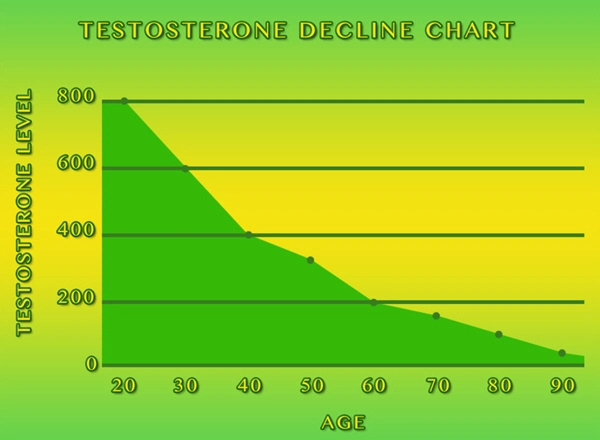
Examples of symptoms of hypogonadism include delayed, reduced, or absent puberty, low libido, and infertility.
Treatment of HH is usually with hormone replacement therapy, consisting of androgen and estrogen administration in males and females, respectively.[3]
See original here:
Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism - Wikipedia, the free ...
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- BioSante Pharmaceuticals, Inc. to Present at BIO Investor Forum [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 9th, 2012]
- Secondary osteoporosis: More than what meets the eye! [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 10th, 2012]
- Trimel Provides Clinical and Operational Update [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 15th, 2012]
- Obese teen boys likelier to become impotent and infertile adults [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 17th, 2012]
- Obese teen boys have up to 50 percent less testosterone than lean boys [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 17th, 2012]
- Trimel Reports Physician Market Research Results for CompleoTRT(TM) [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 24th, 2012]
- Obese teen boys likelier to turn into 'impotent' men [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 24th, 2012]
- Trimel Pharmaceuticals Corporation to Report Third Quarter 2012 Results and Host a Conference Call to Update Investors [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Peer Exchange: Establishing Bone Health Clinics - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- What is hypogonadism and how does it affect fertility? - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Low Testosterone in Men or Man-O-Pause - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Propecia (Finasteride) -- Undisclosed Mechanisms, Potential Dangers [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- How to Get Ripped - Why You Shouldnt Use Anabolic Steroids - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Future Doc: Andropause Alternatives with Dr. James Biddle Part 1 - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Increase Testosterone Naturally With these Diet And Workout Secrets - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Sector Update: Healthcare - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Signs And Symptoms of Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Auxilium and Pfizer Will Conclude Agreement on XIAPEX® EU Collaboration [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 9th, 2012]
- Repros Therapeutics Inc.(R) Reports Third Quarter 2012 Financial Results [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 14th, 2012]
- hypogonadotropic hypogonadism - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 22nd, 2012]
- Research and Markets: Male Hypogonadism - Pipeline Review, H2 2012 [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 30th, 2012]
- Auxilium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. to Present At The Oppenheimer 23rd Annual Growth Conference [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 8th, 2012]
- Low Testosterone (Hypogonadism) - Part 2 - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 10th, 2012]
- The National Mesothelioma Law Firm of Baron and Budd Reports on a New Drug that Could Improve the Health of ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 19th, 2012]
- Hypogonadism ¦ Treatment and Symptoms - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2013]
- Research and Markets: Male Hypogonadism Global Clinical Trials Review, H1, 2013 [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 1st, 2013]
- Male hypogonadism Prof Ossama Fouda - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 9th, 2013]
- Low Testosterone (Hypogonadism) - Part 3 - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 2nd, 2013]
- Hypogonadism - what should you do - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 2nd, 2013]
- NURS805 Hypogonadism Lecture - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 16th, 2013]
- Hypogonadism: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2013]
- Hypogonadism - Diseases & Conditions - Medscape Reference [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 10th, 2013]
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 10th, 2013]
- Low Testosterone (Low-T) Normal Levels, Hypogonadism, Symptoms ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 15th, 2013]
- HYPOGONADISM - University of Dundee [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 23rd, 2013]
- FAQ - Hypogonadism - MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICINAL PLANTS [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 23rd, 2013]
- Hypogonadism - About.com Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 2nd, 2013]
- Exciting medical advances using HRT [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 12th, 2013]
- Male hypogonadism: Symptoms - MayoClinic.com [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 12th, 2013]
- Audio-Digest Foundation Announces the Release of Oncology Volume 04, Issue 16: Highlights from Future Directions ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 15th, 2013]
- Hypogonadism - Medscape Reference [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 21st, 2013]
- Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 23rd, 2013]
- Hypogonadism - HealthCentral [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 24th, 2013]
- Hypogonadism | Medscape - Latest Medical News, Clinical Trials ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 30th, 2013]
- Hypogonadism - SharedJourney [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 23rd, 2014]
- Study Finds Potential Heart Risks from Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 3rd, 2014]
- Endocrine Society calls for large-scale studies to evaluate testosterone therapy risks [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 8th, 2014]
- Testosterone Therapy Not Always Good for Older Men [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 11th, 2014]
- Hypogonadism: Types, Causes, & Symptoms Healthline [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2014]
- Low Testosterone (Hypogonadism) in Men - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2014]
- Hypogonadism : Types, Causes, & Symptoms - Healthline [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 17th, 2014]
- Hypogonadism | Medscape - Latest Medical News, Clinical ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 23rd, 2014]
- Endo: FDA Oks AVEED Injection For Treatment Of Adult Men With Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2014]
- Unit Project 1 Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2014]
- Update on Endo's Product Portfolio - Analyst Blog [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2014]
- Male hypogonadism Symptoms - Diseases and Conditions ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2014]
- Hypogonadism: Types, Causes, & Symptoms - Medical ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2014]
- VLog #127 Frances Explains Hypogonadism. - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2014]
- Repros Completes Enrollment for Androxal Study - Analyst Blog [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2014]
- Prevalence, Diagnosis and Treatment of Hypogonadism in ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 30th, 2014]
- Repros Therapeutics Q2 Loss a Penny Wider than Expected - Analyst Blog [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 12th, 2014]
- Repros Reports Encouraging Late-Stage Data on Androxal - Analyst Blog [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 28th, 2014]
- Repros Therapeutics Analyst Brief Report; Androxal(R) Achieves Superiority in Top Line Analysis by Small Cap Street ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: September 30th, 2014]
- The Wall Street Journal: Repros Therapeutics shares drop on drug application setback [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 18th, 2014]
- Apricus expands development pipeline with in-licensing of US rights for fispemifene [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 21st, 2014]
- Apricus expands development pipeline with the in-licensing of US rights for fispemifene, a phase 2b ready asset, from ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 21st, 2014]
- Hypogonadism No Moustache! No Beard!! [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 28th, 2014]
- Male Hypogonadism: Male Reproductive Endocrinology: Merck ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 28th, 2014]
- Hypogonadism Wikipedia [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 28th, 2014]
- Urology Care Foundation - Urology A-Z - Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2014]
- Will Repros (RPRX) Miss Estimates This Earnings Season? - Analyst Blog [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 5th, 2014]
- Hypogonadism in men living with HIV - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 7th, 2014]
- Male Hypogonadism Therapeutic Pipeline Industry Review, H2 2014 - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 7th, 2014]
- Testosterone Deficiency (Hypogonadism) Overview ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 23rd, 2014]
- Endo to Acquire Rights to Testosterone Nasal Gel Natesto - Analyst Blog [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 26th, 2014]
- Male hypogonadism pathophysiology - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 14th, 2015]
- Auxilium Announces Results from Special Meeting of Stockholders [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 28th, 2015]
- What is Hypogonadism - Symptoms and Treatment | Hormone ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 30th, 2015]
- Male Hypogonadism 1/28/15 - Video [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 31st, 2015]
- Male hypogonadism: symptoms, cause, treatment, risk ... [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2015]
Word Count: 179