Introduction
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), often referred to as age-related low testosterone, is a condition that affects a significant number of American men as they age. Characterized by a decline in testosterone levels, LOH can lead to a variety of symptoms, including reduced libido, fatigue, and decreased muscle mass. Recent studies have begun to explore the role of lifestyle factors, particularly physical activity, in mitigating the onset and severity of this condition. This article delves into the relationship between regular exercise and the prevention of LOH, providing American men with insights into how they can maintain their hormonal health through physical activity.
Understanding Late-onset Hypogonadism
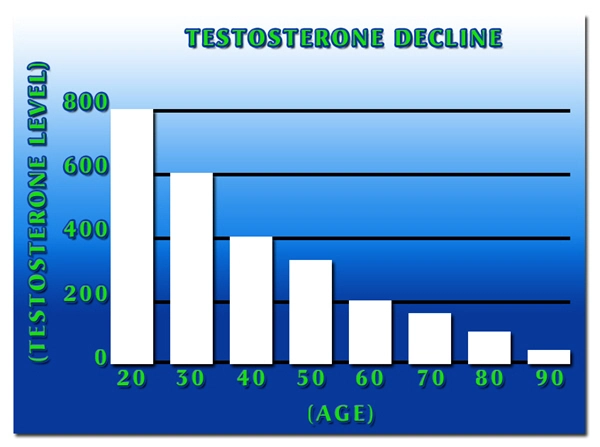
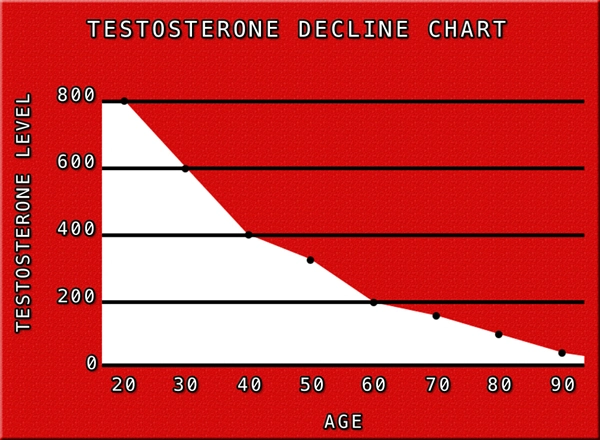
Late-onset hypogonadism is a clinical and biochemical syndrome associated with advancing age and characterized by symptoms and a deficiency in serum testosterone levels. It affects approximately 20% of men over the age of 60, with the prevalence increasing with age. The symptoms of LOH can significantly impact quality of life, making the search for preventive measures crucial.
The Role of Exercise in Hormone Regulation
Exercise has long been recognized as a cornerstone of health and wellness, but its specific impact on hormone levels, particularly testosterone, is a subject of growing interest. Regular physical activity, especially resistance training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT), has been shown to increase testosterone levels in men. This effect is thought to be due to the stimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which is responsible for regulating testosterone production.
Study Findings on Exercise and LOH
A recent study focusing on American men aged 40 to 70 found a significant correlation between regular exercise and higher testosterone levels. Participants who engaged in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week, combined with muscle-strengthening exercises twice a week, showed a lower incidence of LOH compared to their sedentary counterparts. The study also highlighted that the type of exercise mattered, with resistance training showing the most pronounced effect on testosterone levels.
Mechanisms Behind Exercise-Induced Testosterone Boost
The mechanisms by which exercise influences testosterone levels are multifaceted. Firstly, exercise increases blood flow and oxygen delivery to the muscles, which can enhance the function of the Leydig cells in the testes, where testosterone is produced. Secondly, physical activity can reduce body fat, which is known to be inversely related to testosterone levels. Finally, exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation, both of which are linked to better hormonal health.
Practical Recommendations for American Men
For American men looking to prevent or mitigate the effects of LOH, incorporating regular exercise into their routine is essential. The following recommendations can serve as a guide:
- **Engage in Resistance Training:** Aim for at least two sessions per week, focusing on compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses.
- **Incorporate HIIT:** High-intensity interval training can be an effective way to boost testosterone levels. Consider adding HIIT sessions to your weekly routine.
- **Maintain a Balanced Exercise Regimen:** Combine aerobic activities with strength training to maximize the benefits on hormonal health.
- **Monitor Progress and Adjust Accordingly:** Regularly assess your fitness levels and hormone status with the help of a healthcare provider to tailor your exercise plan effectively.
Conclusion
The evidence linking regular exercise to the prevention of late-onset hypogonadism in American men is compelling. By adopting a lifestyle that includes consistent physical activity, men can not only improve their overall health but also maintain optimal testosterone levels as they age. As research continues to unfold, the role of exercise in hormonal health becomes increasingly clear, offering a proactive approach to managing the challenges of aging.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Exploring Alternatives to TRT for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Future of Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment: Innovations and Personalized Approaches [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood, Energy, and Quality of Life in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Effects on Muscle Mass and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Economic Impact, and Management Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Preventing Complications of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Strategies and Insights [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy for Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Early Detection and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Benefits, Risks, and Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Challenges and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Stress Exacerbates Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Holistic Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism's Cognitive Impact in American Men: Awareness and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding TRT Benefits and Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Symptoms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Risks, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Early Intervention Benefits for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Importance of Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advocating for Better Late-Onset Hypogonadism Care: A Call to Action for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Maintaining Independence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advanced Technology Enhances LOH Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Intimate Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Cultural Perceptions and Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Holistic Treatment of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Mental Health Professionals [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Family Support Crucial for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Strategies for Career Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Financial Implications and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Peer Support Enhances Life Quality for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Lifestyle Strategies for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Social Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Advocacy and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies to Combat Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding and Managing Emotional Impacts in Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Lifestyle and Medical Interventions for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Care Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Holistic Management Strategies for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact and Strategies for American Men's Sexual Health [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Research, and Future Directions in American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Community Resources and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Professional Lives and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Therapists' Vital Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 587