Introduction
Testosterone deficiency syndrome, also known as hypogonadism, is a prevalent condition among American males that significantly impacts their quality of life. This article delves into the role of hormonal imbalance in the pathogenesis of this syndrome from an endocrine perspective. Understanding the underlying mechanisms is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome
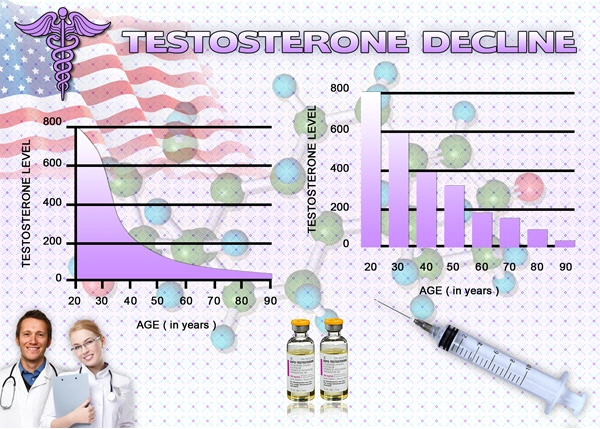
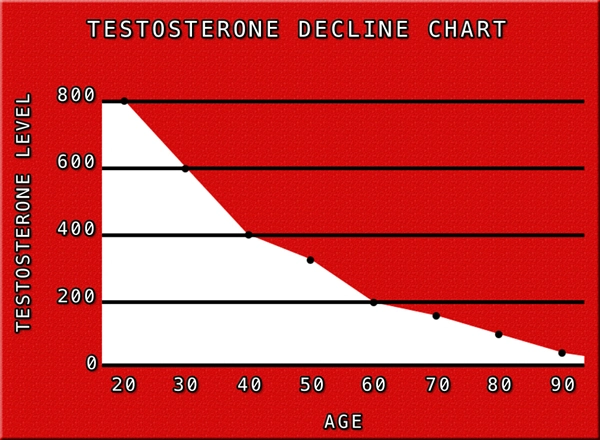
Testosterone deficiency syndrome is characterized by low levels of testosterone, which can lead to a variety of symptoms including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood disturbances. In American males, the prevalence of this condition increases with age, affecting approximately 40% of men over the age of 45. The syndrome can be primary, resulting from testicular failure, or secondary, due to dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
The Role of Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance plays a pivotal role in the development of testosterone deficiency syndrome. The endocrine system, which regulates hormone production and release, is intricately involved in maintaining testosterone levels. Disruptions in this system can lead to decreased testosterone production. Key hormones such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) are essential for stimulating the testes to produce testosterone. When the levels of these hormones are altered, it can result in a cascade of effects leading to testosterone deficiency.
Pathogenesis of Testosterone Deficiency
The pathogenesis of testosterone deficiency involves multiple factors, including genetic predispositions, lifestyle factors, and underlying medical conditions. Obesity, for instance, is a significant risk factor as it can lead to increased aromatization of testosterone to estradiol, thereby reducing circulating testosterone levels. Chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease can also contribute to hormonal imbalances that exacerbate testosterone deficiency.
Endocrine Disruptions and Testosterone Levels
Endocrine disruptions can occur at various levels within the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. For example, stress can lead to increased cortisol levels, which can suppress the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), ultimately affecting testosterone production. Similarly, certain medications, such as opioids and steroids, can interfere with the HPG axis, leading to reduced testosterone levels.
Clinical Implications and Management
Understanding the role of hormonal imbalance in testosterone deficiency syndrome is crucial for effective management. Treatment strategies often involve hormone replacement therapy (HRT), which aims to restore testosterone levels to normal ranges. However, a comprehensive approach that addresses underlying causes, such as lifestyle modifications and management of chronic conditions, is essential for long-term success.
Lifestyle Interventions
Lifestyle interventions play a significant role in managing testosterone deficiency. Regular exercise, particularly resistance training, has been shown to increase testosterone levels. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and diet can help mitigate the effects of obesity on testosterone production. American males are encouraged to adopt these lifestyle changes to improve their hormonal health.
Conclusion
Hormonal imbalance is a critical factor in the pathogenesis of testosterone deficiency syndrome among American males. By understanding the endocrine mechanisms involved, healthcare providers can develop targeted interventions to address this condition effectively. As research continues to evolve, it is hoped that new strategies will emerge to further enhance the management of testosterone deficiency and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
This article underscores the importance of a holistic approach to managing testosterone deficiency, emphasizing the need for both medical and lifestyle interventions. As American males become more aware of the impact of hormonal health on their overall well-being, the demand for comprehensive care will continue to grow.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Understanding Testosterone Deficiency: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Testosterone Decline in American Males: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Hormone Therapy Benefits and Holistic Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Energy-Boosting Treatments [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Mood and Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact, Diagnosis, and Management in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins Linked to Rising Testosterone Deficiency in U.S. Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Muscle Mass and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Prostate Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Importance of Regular Monitoring and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Chronic Illnesses and Their Impact on Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Testosterone and Risk of TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Zinc's Vital Role in Combating Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Magnesium's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Understanding Its Impact on Hair Loss in Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Cognitive Decline in American Men: Impacts and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Muscle, Fat, and Bone Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Libido and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A Promising Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Soy Consumption and Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Depression: Exploring the Link in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Ashwagandha: A Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Growing Concern [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Skin Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Blue Light Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Sleep Apnea: A Bidirectional Health Concern for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Anemia: Understanding Links and Managing Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Weight Training Boosts Testosterone: A Solution for American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Joint Health in American Males: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Male Athletes: Symptoms, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Dental Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Air Pollution's Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Boron Supplementation: A Promising Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Vision Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Pesticide Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Risks and Reduction Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Diet Soda Consumption Linked to Lower Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- EMF Exposure and Testosterone Levels: Implications for TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress and Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- High-Fat Diets and Testosterone: Impacts and Dietary Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Liver Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Pancreatic Health Issues in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Hearing Loss in American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts on Memory and Cognitive Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Heavy Metal Exposure and Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts and Mitigation [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Kidney Function and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Plasticizers Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Emerging Research and Risks [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Adrenal Health: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Thyroid Health: Interconnections and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Fenugreek: A Natural Solution for Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Increased Gallbladder Disease Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Noise Pollution Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: A Growing Concern [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Men: Pituitary Role, Symptoms, and Management [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Tribulus Terrestris: A Promising Aid for Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact, Diagnosis, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Fluoride Exposure and Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Potential Link Explored [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Pineal Gland: Impacts and Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- DHEA Supplementation: A Promising Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Parathyroid Health and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Phthalates Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts on Respiratory Health and COPD [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Bisphenol A Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Ginseng's Potential in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- PFC Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Gastrointestinal Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Urinary Health in American Men: Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Shilajit: A Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Metabolic Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts and Autoimmune Disorder Links [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Triclosan Exposure Linked to Lower Testosterone in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Phytoestrogens' Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact of Endocrine Disruptors on American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Parabens in Personal Care Products Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Cordyceps: A Natural Supplement for Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Neurological Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Understanding Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Genetic and Environmental Factors in Testosterone Deficiency Among American Males: Twin Study Insights [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]
Word Count: 553