Introduction
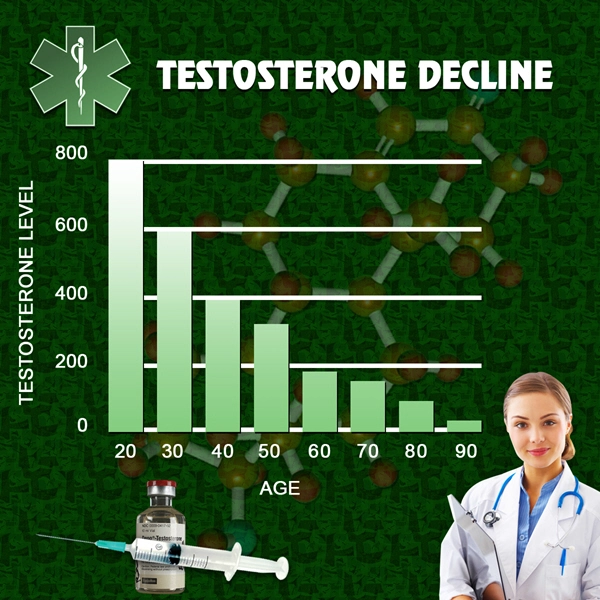
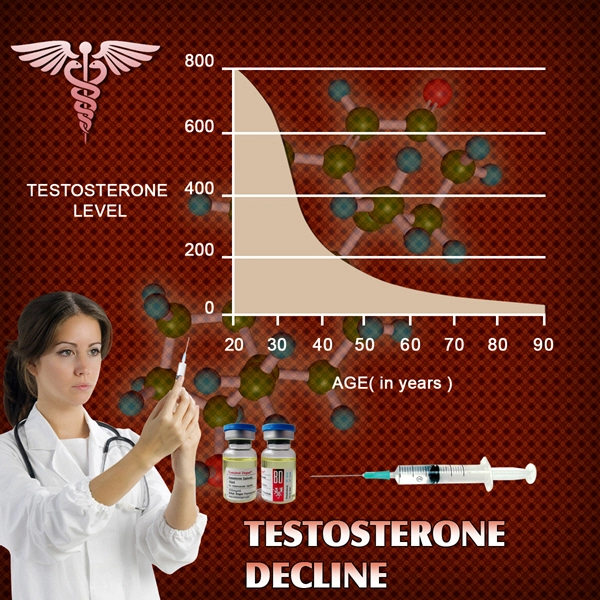
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), commonly known as age-related low testosterone, is a clinical and biochemical syndrome characterized by a deficiency in serum testosterone levels in conjunction with specific symptoms and signs. This condition predominantly affects middle-aged and older men. Recent studies have begun to elucidate a significant association between LOH and diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder prevalent among American males. This article delves into the intricate relationship between these two conditions and offers practical strategies for managing blood glucose levels effectively.
Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Its Prevalence
Late-onset hypogonadism is increasingly recognized as a health concern among American males, with prevalence rates rising as the population ages. Symptoms of LOH include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and loss of muscle mass. These symptoms can significantly impair the quality of life and contribute to other health issues, including diabetes.
The Connection Between LOH and Diabetes
Emerging research has highlighted a bidirectional relationship between LOH and diabetes. Men with LOH are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes due to the role of testosterone in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Conversely, diabetes can exacerbate the symptoms of LOH by further lowering testosterone levels. This vicious cycle underscores the importance of addressing both conditions concurrently.
Mechanisms Linking LOH and Diabetes
The mechanisms linking LOH and diabetes are multifaceted. Testosterone plays a crucial role in maintaining insulin sensitivity and regulating glucose metabolism. Low testosterone levels can lead to increased visceral fat accumulation, which is a known risk factor for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, the inflammatory state associated with diabetes can further suppress testosterone production, perpetuating the cycle of hormonal imbalance and metabolic dysfunction.
Strategies for Managing Blood Glucose Levels in Men with LOH
Effective management of blood glucose levels in men with LOH requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the hormonal and metabolic aspects of the condition. Here are some key strategies:
1. Regular Monitoring and Screening
Men with LOH should undergo regular screening for diabetes, including fasting blood glucose tests and hemoglobin A1c measurements. Early detection of diabetes can facilitate timely intervention and prevent complications.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is paramount for managing both LOH and diabetes. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while limiting processed foods and sugars. Regular physical activity, particularly resistance training, can help improve insulin sensitivity and boost testosterone levels.
3. Weight Management
Obesity is a common risk factor for both LOH and diabetes. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and testosterone levels. Even modest weight loss can yield substantial health benefits.
4. Pharmacological Interventions
In some cases, pharmacological interventions may be necessary. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can be considered for men with clinically confirmed LOH, but it should be administered under strict medical supervision due to potential side effects and contraindications. For diabetes management, medications such as metformin may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity.
5. Collaborative Care
Managing LOH and diabetes often requires a collaborative approach involving endocrinologists, diabetologists, and primary care physicians. Regular follow-ups and adjustments to treatment plans are essential to ensure optimal management of both conditions.
Conclusion
The connection between late-onset hypogonadism and diabetes in American males is a critical area of focus for healthcare providers. Understanding the bidirectional relationship between these conditions can guide effective management strategies that address both hormonal and metabolic health. By implementing regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications, weight management, pharmacological interventions, and collaborative care, men with LOH can better manage their blood glucose levels and improve their overall quality of life.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Exploring Alternatives to TRT for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Future of Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment: Innovations and Personalized Approaches [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood, Energy, and Quality of Life in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Effects on Muscle Mass and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Economic Impact, and Management Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Preventing Complications of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Strategies and Insights [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy for Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Early Detection and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Benefits, Risks, and Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Challenges and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Stress Exacerbates Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Holistic Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism's Cognitive Impact in American Men: Awareness and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding TRT Benefits and Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Symptoms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Risks, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Early Intervention Benefits for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Importance of Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advocating for Better Late-Onset Hypogonadism Care: A Call to Action for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Maintaining Independence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advanced Technology Enhances LOH Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Intimate Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Cultural Perceptions and Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Holistic Treatment of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Mental Health Professionals [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Family Support Crucial for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Strategies for Career Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Financial Implications and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Peer Support Enhances Life Quality for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Lifestyle Strategies for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Social Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Advocacy and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies to Combat Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding and Managing Emotional Impacts in Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Lifestyle and Medical Interventions for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Care Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Holistic Management Strategies for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact and Strategies for American Men's Sexual Health [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Research, and Future Directions in American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Community Resources and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Professional Lives and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Therapists' Vital Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 592