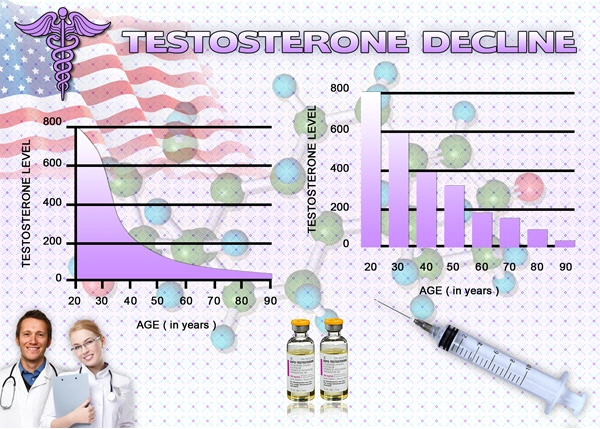
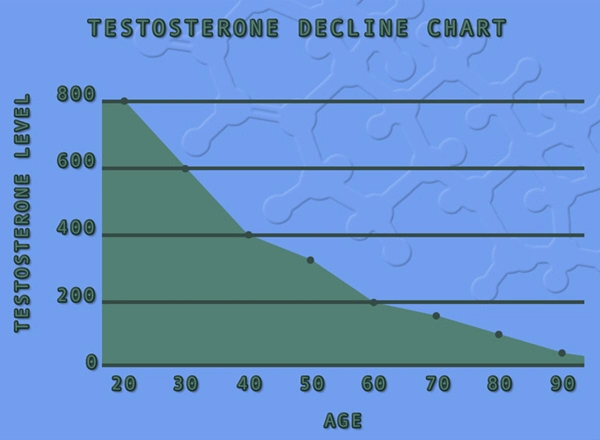
Introduction
Testosterone propionate, a synthetic derivative of the primary male sex hormone, has been widely utilized in medical and athletic communities for its anabolic and androgenic properties. Its impact on hair growth and pattern, particularly in American males, has been a subject of extensive research due to its potential to influence androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male pattern baldness. This article delves into a longitudinal study spanning a decade, examining the nuanced effects of testosterone propionate on hair dynamics in this demographic.
Study Design and Methodology
The study followed a cohort of 500 American males aged between 25 and 45 years, who were administered testosterone propionate under medical supervision. Participants were monitored annually through clinical examinations, photographic assessments, and self-reported surveys to track changes in hair growth and pattern. The study aimed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the long-term effects of testosterone propionate on hair health.
Findings on Hair Growth
Over the decade, the study observed varied responses to testosterone propionate in terms of hair growth. Approximately 30% of participants reported an increase in hair density, particularly in areas not typically affected by male pattern baldness, such as the beard and body hair. This suggests that testosterone propionate may enhance hair growth in androgen-sensitive regions. However, the response was not uniform, indicating individual variability in sensitivity to the hormone.
Impact on Hair Pattern
The most significant finding was the influence of testosterone propionate on hair pattern, particularly in the scalp. About 45% of participants experienced accelerated hair loss in the frontal and vertex regions, consistent with the progression of androgenetic alopecia. This suggests that testosterone propionate may exacerbate male pattern baldness in susceptible individuals. Conversely, 20% of participants showed no change in hair pattern, highlighting the complex interplay between genetics and hormonal influence.
Mechanisms of Action
Testosterone propionate is converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. DHT is a more potent androgen that binds to receptors in hair follicles, potentially leading to miniaturization and eventual hair loss in genetically predisposed individuals. The study's findings align with this mechanism, as participants with a genetic predisposition to androgenetic alopecia were more likely to experience hair loss.
Clinical Implications
The study's results have significant implications for clinicians prescribing testosterone propionate. It underscores the need for a thorough assessment of a patient's genetic predisposition to hair loss before initiating treatment. Additionally, patients should be counseled on the potential for accelerated hair loss and offered strategies for mitigation, such as the use of 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors.
Patient Perspectives and Quality of Life
Participants' self-reported surveys revealed a range of emotional responses to the observed changes in hair growth and pattern. While some appreciated the increased body hair, others were distressed by the accelerated scalp hair loss. This highlights the importance of addressing the psychological impact of hair changes in patients receiving testosterone propionate.
Conclusion
The longitudinal study provides valuable insights into the effects of testosterone propionate on hair growth and pattern in American males. While it can enhance hair growth in certain areas, it may also accelerate male pattern baldness in susceptible individuals. Clinicians must consider these findings when prescribing testosterone propionate and provide comprehensive care that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of hair health.
Future Directions
Further research is needed to explore the genetic factors that influence individual responses to testosterone propionate and to develop targeted therapies that can mitigate its adverse effects on hair. Additionally, long-term studies with larger cohorts could provide more robust data on the prevalence and severity of hair-related side effects.
This study underscores the complexity of hormonal influences on hair dynamics and the need for personalized approaches in the management of patients receiving testosterone propionate.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Male Health and Managing Hormonal Imbalances in American Men [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Sleep Quality in American Males: A Therapeutic Overview [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Role in Male Pattern Baldness: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Long-term Testosterone Propionate Use: Health Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Ethical Considerations of Testosterone Propionate Use in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Potential Solution for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Comprehensive Guide for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Energy Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Legal Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Male Fertility in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Liver Health: Risks and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Anemia in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Male Aesthetics and Muscle Growth in America [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Recovery and Performance in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Therapy for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Blood Pressure in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Health in American Men Under Medical Supervision [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Exploring Its Role in Stress Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Immune Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Diabetes Risk in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Effects on Mood and Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Vitality and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Cholesterol Levels in American Men: Cardiovascular Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Strength and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate in HRT: Benefits, Risks, and Legal Aspects for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Mental Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Aid in Managing Obesity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Joint Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Fitness and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Administration, and Risks for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Dosage, Side Effects for American Male Bodybuilders [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Mental Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Performance and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Fertility in American Males with Low Sperm Count [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Bone Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Legal Issues for American Weightlifters [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate in Anti-Aging: Benefits, Risks, and Optimal Use in Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Endurance in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Managing Hormonal Imbalances in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Muscle Recovery in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Chronic Fatigue in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Health in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Muscle Wasting in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Boosting Energy in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Libido and Sexual Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Muscle Growth and Strength in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits and Risks for Managing Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Cardiovascular Impacts and Risks in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Mood and Emotional Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Health and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Ethics in Athletic Performance Enhancement [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate Boosts Bone Density in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Desire and Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Managing Deficiency in American Men - Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Fatigue in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Medical Uses, Fitness Benefits, and Regulatory Considerations [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Muscle Strength and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate in HRT: Benefits, Risks, and Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Treating Muscle Loss in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sports Performance and Associated Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on American Men's Psychological Health: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Strength Training in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Cardiovascular Risks and Benefits in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Impacts on American Men's Reproductive Health and Beyond [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: A Promising Treatment for Sarcopenia in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Cardiovascular Benefits and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Combating Lethargy in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Uses, Benefits, and Risks in Men's Health Programs [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Sexual Vitality in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Impact on Bone Density and Joint Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Benefits, Risks, and Regulation for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate: Managing Hormonal Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Propionate's Efficacy in Treating Osteoporosis in American Males: A Decade-Long Study [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 603