Introduction
Andropause, commonly referred to as male menopause, is a term used to describe the gradual decline in testosterone levels that many men experience as they age. This phenomenon has been increasingly recognized for its wide-ranging effects on men's health, including its potential association with hair loss, or alopecia. A comprehensive 20-year study focusing on American males has shed light on the correlation between these hormonal changes and the incidence of hair loss, offering valuable insights into this prevalent concern.
Study Overview and Methodology
The study, conducted over two decades, involved a cohort of 5,000 American males aged between 40 and 70 years at the outset. Participants were assessed annually for testosterone levels, symptoms of andropause, and the extent of hair loss. The research utilized advanced biochemical assays to measure hormone levels and employed standardized scales to quantify hair loss, ensuring a robust and reliable dataset.
Key Findings on Andropause and Testosterone Levels
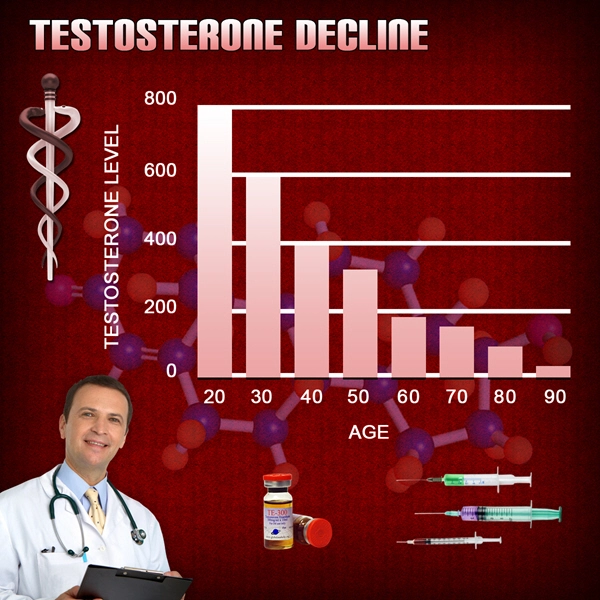
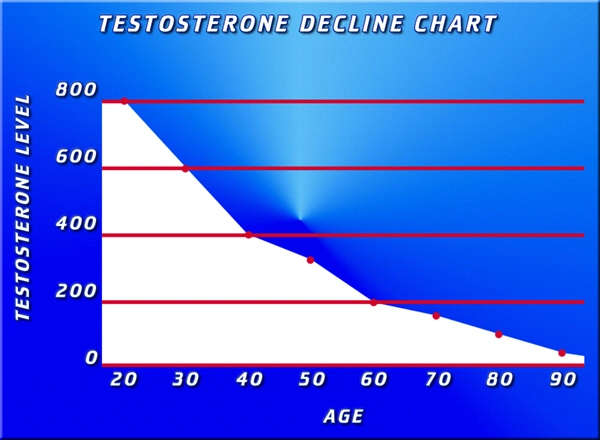
The data revealed a significant decline in testosterone levels among the participants over the 20-year period. On average, testosterone levels decreased by approximately 1% per year, aligning with previous research on andropause. This decline was associated with various symptoms, including reduced libido, fatigue, and mood changes, underscoring the multifaceted impact of hormonal shifts in aging men.
Correlation Between Andropause and Hair Loss
One of the most striking findings of the study was the strong correlation between declining testosterone levels and the incidence of hair loss. Men with the most significant drops in testosterone were found to be three times more likely to experience noticeable hair loss compared to those with more stable hormone levels. This association suggests that andropause may play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of alopecia in aging males.
Mechanisms Linking Hormonal Changes to Alopecia
The study delved into the biological mechanisms that may underlie the link between andropause and hair loss. It was hypothesized that the decline in testosterone could lead to an imbalance in other hormones, such as dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is known to contribute to hair follicle miniaturization and eventual hair loss. Additionally, the study explored the potential role of inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which may be exacerbated by hormonal changes and could further contribute to alopecia.
Implications for Clinical Practice and Future Research
The findings of this study have significant implications for the clinical management of hair loss in aging men. Healthcare providers should consider assessing testosterone levels in men presenting with hair loss, particularly those in their 40s and beyond. This approach could lead to earlier detection of andropause and more targeted interventions, such as hormone replacement therapy, which may help mitigate both the symptoms of andropause and associated hair loss.
Furthermore, the study highlights the need for continued research into the complex interplay between hormones and hair health. Future studies should aim to elucidate the specific pathways through which testosterone influences hair follicle function and explore novel therapeutic strategies that address the root causes of andropause-related alopecia.
Conclusion
The 20-year study on American males has provided compelling evidence of a significant correlation between andropause and hair loss. By shedding light on the hormonal underpinnings of alopecia in aging men, this research not only enhances our understanding of male health but also paves the way for more effective and personalized treatment approaches. As the population continues to age, addressing the challenges posed by andropause and its associated conditions, such as hair loss, will remain a critical focus for medical science and public health initiatives.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Understanding Andropause: Male Menopause, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Andropause in American Males: Myths, Realities, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Andropause in American Men: Supplements and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Managing Andropause: Diet, Exercise, Stress, and Hormone Therapy Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Navigating Andropause: Understanding Emotional Changes and Support Strategies for Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Andropause and Depression: Symptoms, Interventions, and Empowerment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Andropause: Embracing Male Menopause as a Growth Opportunity for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Andropause Management: Importance of Regular Check-ups for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Andropause and Diabetes Risk in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Andropause and Prostate Health: Understanding the Link and Managing Symptoms [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Managing Andropause: Boosting Energy and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Andropause and Cognitive Health: Strategies for American Men to Maintain Mental Sharpness [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Andropause: Managing Emotional Well-being in American Men Through Diet, Exercise, and Support [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Andropause: Navigating Social Impacts and Coping Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Andropause: Building Support Networks for American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Andropause Effects on Skin: Understanding and Managing Changes in Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Andropause and Hair Loss: Understanding Causes and Exploring Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Andropause: Mental Health Professionals' Role in Managing Psychological Impact [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Andropause: A Guide for American Males to Discuss with Healthcare Providers [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Andropause and Digestive Health: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hydration's Crucial Role in Managing Andropause Symptoms and Enhancing Well-being [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Andropause in American Males: Managing Muscle Loss and Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Its Impact on Energy Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Andropause: Understanding and Managing Male Menopause Effects on American Men's Lives [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Andropause in American Men: Enhancing Sleep Quality for Symptom Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Andropause Impact on Kidney Health: Symptoms, Management, and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Andropause and Joint Health: Strategies for American Men to Maintain Vitality [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Andropause and Memory: Strategies for Enhancing Recall in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Andropause: Exercise Benefits and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Andropause: Stress Reduction Techniques for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Andropause and Liver Health: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Andropause and Cholesterol: Management Strategies for Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Andropause: Importance of Screenings and Lifestyle Changes for Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Andropause and Thyroid Function: Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Andropause and Vision: Managing Eye Health in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Andropause: Understanding and Managing Declining Motivation in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Andropause Management: Benefits and Risks of Hormone Replacement Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Andropause: Nutrition and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Andropause: Symptoms, Causes, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and the Importance of Community Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Andropause: Managing Symptoms and Balancing Work-Life for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Andropause and Self-Esteem: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Andropause: Managing Mental Health and Breaking Stigma in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Andropause and Emotional Intelligence: Navigating Challenges for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Andropause and Respiratory Health: Symptoms, Links, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Mindfulness: A Holistic Approach to Managing Andropause Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Its Impact on American Men's Confidence [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Andropause and Immune Health: Strategies for American Males to Boost Well-being [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Andropause: Understanding Symptoms, Family Support, and Healthy Lifestyle Changes for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Andropause and Blood Pressure: Monitoring and Management Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Andropause and Hearing Loss: Understanding the Link in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Andropause and Dental Health: Essential Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hobbies: A Vital Tool for Managing Andropause in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Andropause in American Men: Impact on Creativity and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Andropause and Allergies: Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life in American Males [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Navigating Andropause: Setting Goals for Health, Career, and Relationships [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Andropause: Managing Time Effectively to Enhance Life Quality in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Andropause: Navigating Male Menopause and Its Impact on American Men's Lives [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Andropause Impact on Foot Health: Prevention and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Andropause and Lifelong Learning: Enhancing Life Quality for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Technology's Role in Managing Andropause for American Men: Wearables to Digital Therapeutics [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Andropause Effects on Hand Health: Symptoms, Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Volunteering: A Holistic Approach to Managing Andropause in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Andropause and Skin Sensitivity: Managing Symptoms in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Andropause: Understanding Its Impact on American Men's Adventurous Spirit [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Andropause and Eye Health: Impacts and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Andropause Effects on Nail Health: Nutritional and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Travel as Therapy: Managing Andropause in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Andropause and Nasal Health: Understanding the Link and Managing Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Andropause: Understanding Testosterone Decline and Its Impact on Men's Humor and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Andropause Impact on Throat Health: Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Music Therapy: A Holistic Approach to Managing Andropause Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Andropause: Financial Planning Strategies for American Men's Health and Retirement [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Andropause Effects on Oral Health: Understanding Tongue Changes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Art Therapy: A Holistic Approach to Managing Andropause in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Andropause: Navigating Testosterone Decline and Identity in American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Andropause in American Men: Navigating Social Isolation and Building Connections [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Andropause Effects on Ear Health: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Andropause and Cognitive Decline: Insights from a 20-Year Study on American Men [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]
- 20-Year Study Reveals Andropause's Impact on Employment, Income, and Quality of Life in American Males [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]
Word Count: 573