Introduction
The intricate relationship between endocrinology and diabetes has long been a subject of intense research and clinical interest. In American men, the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes has been steadily increasing, prompting a closer examination of the underlying factors contributing to this trend. One area of particular focus is the role of hormonal imbalances in the development and progression of this chronic condition. This article delves into the complex interplay between endocrinology and diabetes, shedding light on the specific hormonal factors that may predispose American men to Type 2 diabetes.
The Role of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, a hallmark of Type 2 diabetes, is closely linked to hormonal imbalances in American men. Elevated levels of certain hormones, such as cortisol and catecholamines, can contribute to the development of insulin resistance. Chronic stress, a common issue among American men, can lead to increased cortisol production, which in turn can impair insulin sensitivity. Additionally, the sympathetic nervous system, responsible for the "fight or flight" response, can release catecholamines that interfere with insulin action. Understanding these hormonal influences is crucial for developing effective prevention and management strategies for Type 2 diabetes in American men.
Testosterone and Glucose Metabolism
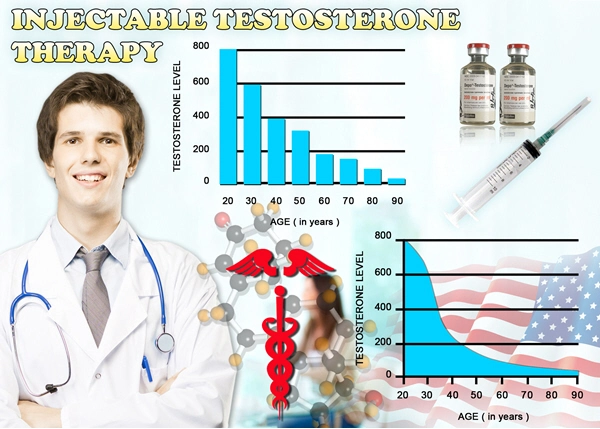
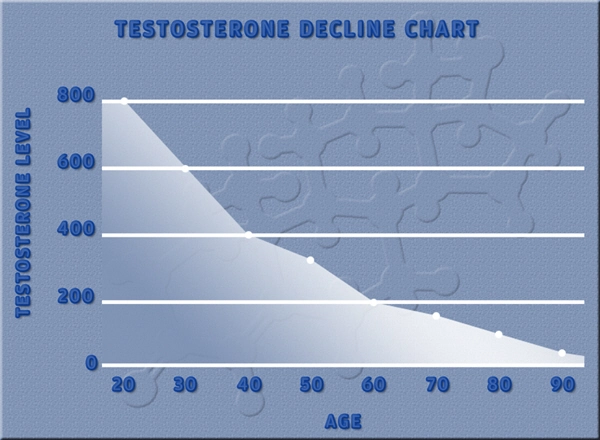
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a significant role in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Studies have shown that low testosterone levels are associated with an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes in American men. Hypogonadism, a condition characterized by low testosterone, can lead to insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance. Furthermore, testosterone replacement therapy has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control in hypogonadal men with Type 2 diabetes. These findings underscore the importance of maintaining optimal testosterone levels for metabolic health in American men.
The Impact of Obesity and Adipokines
Obesity, a major risk factor for Type 2 diabetes, is closely linked to hormonal imbalances in American men. Adipose tissue, particularly visceral fat, produces adipokines that can influence insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Leptin, an adipokine that regulates appetite and energy balance, has been shown to be elevated in obese individuals, contributing to insulin resistance. Conversely, adiponectin, another adipokine, has insulin-sensitizing properties and is often reduced in obese individuals. Understanding the role of adipokines in the development of Type 2 diabetes can help guide targeted interventions for American men struggling with obesity and metabolic dysfunction.
The Influence of Growth Hormone and IGF-1
Growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) are key players in the regulation of glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. In American men, alterations in GH and IGF-1 levels have been associated with an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Acromegaly, a condition characterized by excessive GH production, can lead to insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. Conversely, GH deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes. IGF-1, which is primarily produced in response to GH stimulation, has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Maintaining optimal levels of GH and IGF-1 is essential for preserving metabolic health in American men.
Conclusion
The link between endocrinology and diabetes in American men is a complex and multifaceted issue. Hormonal imbalances, including those involving insulin resistance, testosterone, adipokines, growth hormone, and IGF-1, play a significant role in the development and progression of Type 2 diabetes. By understanding these hormonal influences, healthcare providers can develop targeted prevention and management strategies to address the growing burden of Type 2 diabetes in American men. Further research is needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms underlying these hormonal imbalances and to identify novel therapeutic approaches for improving metabolic health in this population.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Clomiphene Citrate Therapy in Men: Enhancing Endocrine Function in Secondary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2025]
- Comprehensive Endocrine Evaluation Essential for Diagnosing Fatigue in American Men [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Exploring hCG Monotherapy and Exogenous Testosterone in Young Men with Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: A Focus on Testicular Function [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- The Crucial Link Between Insulin Resistance and Male Hormonal Imbalances: Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- The Crucial Link: Vitamin D's Impact on Androgen Metabolism and Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- The Critical Balance: Cortisol and Testosterone's Impact on Men's Health and Hormones [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Exploring Neurosteroid Modulation as a Pioneering Treatment for Stress-Induced Endocrine Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) in Male Endocrine Disorders [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Exploring the Role of Oxytocin in Male Endocrinology: From Physiology to Therapeutic Potential [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Precision Medicine Revolutionizes HRT for Male Endocrine Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Impact on Male Health and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Adipokines and Male Endocrine Health: Mechanisms, Impacts, and Therapeutic Prospects [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Chronobiology's Role in Male Hormone Secretion and Endocrinology for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Trace Elements' Impact on Hormone Metabolism in American Men: Zinc, Selenium, Magnesium [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Gut Microbiome's Role in Men's Steroid Hormone Metabolism and Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Thyroid-Testicular Axis: Impact on Male Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Somatostatin Analogues: Versatile Applications in Male Endocrinology and Beyond [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Inflammaging and Male Hormonal Health: Strategies for Endocrine Optimization [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Mitochondrial Health and Male Hormones: Therapeutic Targets for Age-Related Decline [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Metabolomics Revolutionizing Male Endocrine Health Diagnostics and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- OSA in American Men: Exploring Endocrine Effects Beyond Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Ghrelin Modulation Enhances Weight Management in Hypogonadal American Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Energy Balance and Reproductive Function in American Men: Neuroendocrine Integration and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- NAFLD's Impact on Male Endocrine and Reproductive Health: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Male Hormonal Health and Cognitive Function: The Impact of Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Pharmacogenomics Revolutionizes Hormone Therapy in Men: Tailoring Treatment to Genetic Profiles [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- SHBG's Role in Male Hormonal Health: Regulation, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Implications [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Luteinizing Hormone Dynamics: Diagnosis and Treatment in Male Endocrinology [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Polycythemia in Men on Testosterone Therapy: Monitoring and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormone Optimization and Lifestyle Strategies to Combat Sarcopenia in Aging Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Epigenetic Changes from HRT in American Men: Longitudinal Insights and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Leptin Resistance in American Men: Endocrine Effects and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine Reserve Testing: Diagnosis and Management of Hormonal Imbalances in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Optimizing Bone Health: BMD Monitoring Protocols for Men on HRT in the USA [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Male Climacteric Syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Multidisciplinary Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise and Endocrinology in Men: Hormonal Dynamics and HRT Implications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Navigating Prostate Health During Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Risks and Monitoring Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Pituitary Incidentalomas in Men: Evaluation, Management, and Long-term Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Biomarkers in Male Endocrinology: Growth Factors and Cytokines' Clinical Applications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Androgen Receptor Sensitivity: Enhancing Personalized Hormone Therapy in Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Vasopressin's Therapeutic Roles in Male Endocrinology and Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing HPT Axis Recovery in American Men Post-Testosterone Therapy: Endocrinological Approaches [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Diurnal Hormone Patterns: Optimizing Endocrinology for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Post-Traumatic Hypopituitarism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrine Sequelae in Male TBI Patients: Long-Term Management and Follow-Up Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- ECS's Role in Male Reproductive Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Subclinical Endocrinopathies in Men: Diagnosis, Thresholds, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Inhibin B: Key Biomarker for Assessing Male Fertility and Endocrine Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Aging Men's Endocrine Changes: Impacts on Fertility and Offspring Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Opioid-Induced Endocrinopathy in Men: Mechanisms, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Multimarker Approach to Cardiometabolic Risk in Men on Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Endocrine Frailty in Aging Men: Hormonal Decline and Multimodal Intervention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Male Sex Hormones and Autoimmune Disease Management in American Men: Endocrinology Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- HRT and Telomere Length: Implications for Aging and Longevity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- INSL3: A Stable Biomarker for Leydig Cell Function in Male Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Neuropeptide Y: Key Regulator in Male Endocrine and Metabolic Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bioavailable Hormones: Key to Effective Male Endocrinology Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disruption in Men Post-Chemotherapy: Strategies and Support [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Male Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Counseling [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- AMH's Emerging Role in Adult Male Endocrinology and Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hyperparathyroidism's Impact on Male Reproductive Health: Diagnosis and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Radiation-Induced Hypopituitarism in Men: Diagnosis, Hormone Deficiency Patterns, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Hemochromatosis in American Men: Endocrine Effects, Screening, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- CKD's Impact on Male Endocrine Function: Adaptations and Therapeutic Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Male Sexual Desire Disorders: Endocrine Focus and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Osteoporosis in Men: Endocrine Evaluation, Hormone Therapy, and Dietary Management [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Adrenal Incidentalomas in Men: Evaluation, Management, and Long-term Follow-up Strategies [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Cushing's Syndrome in Men: Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Their Impact on Male Stress Urinary Incontinence [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Male Fertility Through Endocrinology [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Enhancing Endocrine Resilience in American Men: Strategies and Biological Insights [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Growth Hormone and IGF-1: Enhancing Male Athletic Performance and Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Endocrine Management of Hormone Therapy for Transgender Men: Protocols and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Androgen Action: Mechanisms, Prostate Health, and Targeted Therapies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Advancements in Male Hormonal Contraception: Impact and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- AI-Driven Precision Endocrinology: Personalizing Hormone Therapy for Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Enhancing Male Endocrinology Care with Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Quality Indicators in Male Endocrine Care: Development, Implementation, and Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Integrative Endocrinology: Holistic Hormone Therapy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Wearable Tech Revolutionizes Hormone Monitoring and HRT for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
Word Count: 586