Introduction
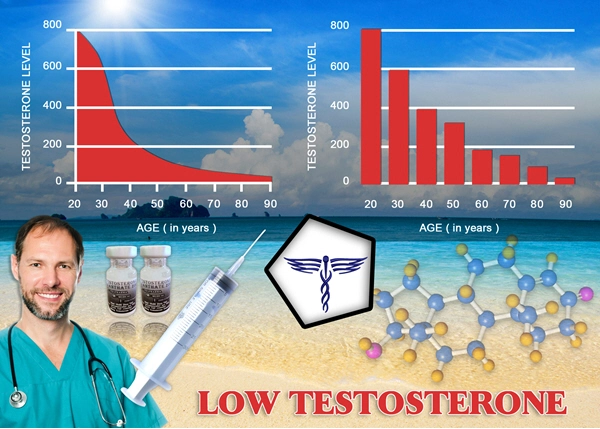
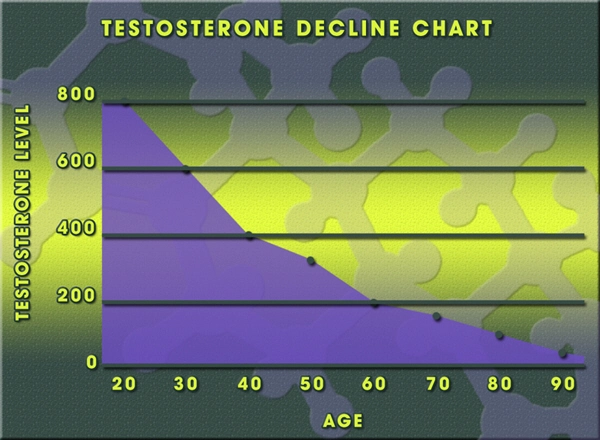
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), commonly known as age-related low testosterone, is a clinical and biochemical syndrome characterized by a deficiency in serum testosterone levels in aging men, which can lead to a variety of symptoms including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood disturbances. As the American male population continues to age, the prevalence of LOH is expected to rise, necessitating effective therapeutic strategies. Hormonal therapies have emerged as a cornerstone in managing LOH, with various modalities available to address the diverse needs of affected individuals. This article provides a comparative analysis of different hormonal treatment options, focusing on their efficacy and safety profiles in American men.
Understanding Late-onset Hypogonadism
Late-onset hypogonadism is a condition that affects many men as they age, typically after the age of 40. It is characterized by a gradual decline in testosterone levels, which can lead to a range of symptoms that impact quality of life. The diagnosis of LOH involves a thorough clinical assessment, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and laboratory testing to confirm low testosterone levels. Early recognition and treatment of LOH are crucial to mitigate its adverse effects on physical and mental health.
Hormonal Therapy Options for LOH
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is the most widely used treatment for LOH. TRT can be administered through various routes, including intramuscular injections, transdermal patches, gels, and oral capsules. Each method has its advantages and considerations. Intramuscular injections provide a steady release of testosterone but require regular clinic visits. Transdermal gels and patches offer convenience and flexibility, though they may cause skin irritation in some users. Oral capsules are a newer option that provides an alternative for those who prefer not to use injections or topical treatments.
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs)
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) are a class of therapeutic compounds that have tissue-selective effects, potentially offering a more targeted approach to treating LOH. SARMs are designed to stimulate anabolic activity in muscle and bone while minimizing the side effects associated with traditional androgen therapies. Although SARMs are still under investigation, preliminary studies suggest they may be a promising option for managing LOH symptoms in American men.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is another hormonal therapy used to treat LOH. hCG stimulates the testes to produce testosterone, which can be beneficial for men who wish to preserve their fertility. Unlike TRT, hCG does not suppress the body's natural production of testosterone, making it a suitable option for younger men with LOH who are considering future fertility.
Comparative Efficacy and Safety Profiles
When comparing the efficacy of different hormonal therapies for LOH, TRT has the most extensive evidence base, demonstrating significant improvements in libido, erectile function, and overall well-being. However, TRT is associated with potential side effects, including erythrocytosis, sleep apnea, and prostate enlargement, which require careful monitoring.
SARMs, while promising, have limited long-term data on their safety and efficacy. Ongoing clinical trials are essential to establish their role in the management of LOH. hCG, on the other hand, offers a fertility-preserving option but may not be as effective as TRT in rapidly alleviating symptoms.
Tailoring Treatment to Individual Needs
The choice of hormonal therapy for LOH should be individualized, taking into account the patient's symptoms, medical history, and treatment goals. For men with severe symptoms and no fertility concerns, TRT may be the most appropriate choice. Those who prioritize fertility preservation may benefit from hCG, while individuals seeking a novel approach might consider participating in clinical trials for SARMs.
Conclusion
Hormonal therapies play a vital role in managing late-onset hypogonadism in American men, offering various options to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. As research continues to evolve, it is essential for healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest developments in hormonal treatments for LOH. By tailoring therapy to the individual needs of each patient, clinicians can optimize outcomes and enhance the well-being of men affected by this common age-related condition.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Exploring Alternatives to TRT for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Future of Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment: Innovations and Personalized Approaches [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood, Energy, and Quality of Life in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Effects on Muscle Mass and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Economic Impact, and Management Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Preventing Complications of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Strategies and Insights [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy for Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Early Detection and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Benefits, Risks, and Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Challenges and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Stress Exacerbates Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Holistic Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism's Cognitive Impact in American Men: Awareness and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding TRT Benefits and Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Symptoms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Risks, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Early Intervention Benefits for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Importance of Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advocating for Better Late-Onset Hypogonadism Care: A Call to Action for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Maintaining Independence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advanced Technology Enhances LOH Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Intimate Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Cultural Perceptions and Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Holistic Treatment of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Mental Health Professionals [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Family Support Crucial for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Strategies for Career Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Financial Implications and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Peer Support Enhances Life Quality for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Lifestyle Strategies for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Social Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Advocacy and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies to Combat Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding and Managing Emotional Impacts in Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Lifestyle and Medical Interventions for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Care Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Holistic Management Strategies for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact and Strategies for American Men's Sexual Health [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Research, and Future Directions in American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Community Resources and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Professional Lives and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Therapists' Vital Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 658