Introduction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), commonly referred to as impotence, is a prevalent issue affecting a significant number of American men. While various factors contribute to ED, recent research has begun to explore the relationship between alcohol consumption and the occurrence of soft erections. This article delves into a longitudinal study that examines how drinking habits among American men influence the prevalence of soft erections, providing insights into the potential impacts of alcohol on sexual health.
Study Design and Methodology
The study in question was conducted over a period of five years, involving a cohort of 2,000 American men aged between 25 and 65. Participants were selected from diverse socio-economic backgrounds to ensure a representative sample. The research utilized a combination of self-reported questionnaires and clinical assessments to gather data on alcohol consumption and the incidence of soft erections. Alcohol intake was categorized into three groups: light, moderate, and heavy drinkers, based on the number of standard drinks consumed per week.
Findings on Alcohol Consumption and Soft Erections
The results of the study revealed a significant correlation between the level of alcohol consumption and the frequency of soft erections. Light drinkers, defined as those consuming up to seven standard drinks per week, showed a minimal increase in the incidence of soft erections compared to non-drinkers. In contrast, moderate drinkers, who consumed between eight and 14 drinks per week, experienced a noticeable increase in soft erections. The most alarming findings were observed among heavy drinkers, those consuming 15 or more drinks per week, who reported a significantly higher prevalence of soft erections.
Mechanisms Linking Alcohol to Soft Erections
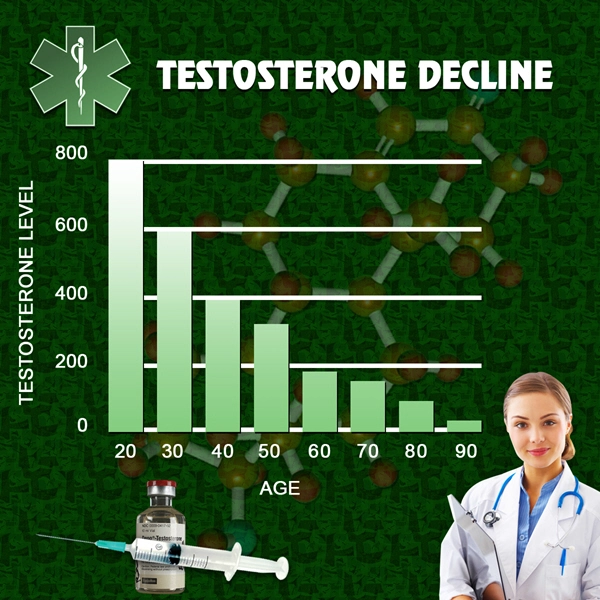
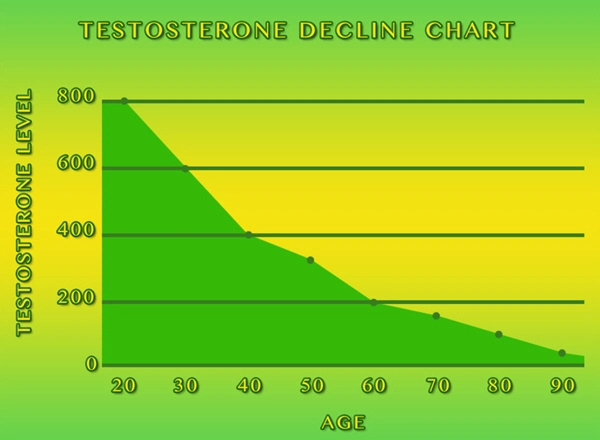
Several physiological mechanisms may explain the observed link between alcohol consumption and soft erections. Alcohol is known to be a depressant that can impair the central nervous system, potentially affecting the neural pathways responsible for achieving and maintaining an erection. Furthermore, chronic alcohol use can lead to hormonal imbalances, such as decreased testosterone levels, which are crucial for sexual function. Additionally, alcohol can cause vascular damage, reducing blood flow to the penis, which is essential for achieving a firm erection.
Implications for Public Health and Clinical Practice
The findings of this study have important implications for public health initiatives and clinical practice. Healthcare providers should consider screening for alcohol consumption when assessing patients with erectile dysfunction. Public health campaigns aimed at reducing alcohol intake could potentially lower the incidence of soft erections among American men. Moreover, men who experience soft erections should be counseled on the potential benefits of reducing alcohol consumption as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Limitations and Future Research Directions
While the study provides valuable insights into the relationship between alcohol consumption and soft erections, it is not without limitations. The reliance on self-reported data may introduce bias, and the study's focus on American men limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future research should aim to include more diverse samples and employ objective measures of alcohol consumption and sexual function. Additionally, longitudinal studies that track changes in drinking habits over time could further elucidate the causal relationship between alcohol and soft erections.
Conclusion
The longitudinal study on American men's drinking habits and the prevalence of soft erections underscores the significant impact of alcohol consumption on sexual health. By highlighting the increased risk of soft erections associated with moderate to heavy drinking, the research provides a compelling case for moderating alcohol intake. As awareness of this link grows, both healthcare professionals and the public can take steps to address this issue, potentially improving the quality of life for many American men.
In summary, the study serves as a crucial reminder of the broader health implications of alcohol consumption and the importance of considering lifestyle factors in the management of erectile dysfunction.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Demystifying the Enigma of Soft Erections: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Exploring the Mind-Body Connection: Harnessing Meditation and Mindfulness for Enhanced Erections [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Male Potency: Deciphering the Science behind Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Masculinity Reenvisioned: Soft Erections as an Emblem of Strength [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Revitalizing Virility: Lifestyle Rewiring for Enhanced Erectile Potential [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Whispering Battles: An Introspection into the Private Struggles with Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Stress Matrix: Decoding the Impact of Psychological Stress on Erectile Function [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Unveiling the Hidden Struggles: A Comprehensive Overview of Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Soft Erections in Aging Men: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Enhancing Erectile Function Through Exercise: Understanding Its Physiological and Psychological Benefits [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Exploring Diet's Impact on Erectile Function and Health [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Exploring the Crucial Role of Sleep in Enhancing Male Erectile Function and Health [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Treatments, and Lifestyle Changes [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Optimizing Hormonal Balance for Erectile Health: A Comprehensive Guide for Men's Well-being [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- The Crucial Link Between Vascular Health and Erectile Function: A Comprehensive Exploration [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- The Holistic Connection: Erectile Dysfunction as a Reflection of Overall Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- From Flab to Firm: How Weight Loss Can Enhance Male Sexual Health and Combat Soft Erections [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Debunking Myths: Understanding Soft Erections and Effective ED Treatments for American Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Understanding the Impact of Medications on Male Sexual Health: Navigating Drug-Induced Soft Erections [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Stress and Soft Erections: Understanding Impacts and Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Vitamins and Minerals: Enhancing Male Sexual Health and Erection Quality [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Counseling's Role in Overcoming Soft Erections: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on American Males' Erectile Health and Benefits of Quitting [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Herbal Remedies for Enhancing Erectile Function in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Soft Erections: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Soft Erections in Young Men: Causes, Solutions, and Importance of Professional Help [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Addressing Soft Erections: Communication and Collaborative Strategies for Couples [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Erection Quality: Strategies for Optimal Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Work Stress and Erectile Dysfunction: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Diagnosing Soft Erections: Comprehensive Approaches for American Males' Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Enhancing Erection Quality and Overall Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Enhancing Male Sexual Health: Diet, Exercise, and Lifestyle Strategies for Strong Erections [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Economic Impacts of Erectile Dysfunction on American Men: Costs, Productivity, and Relationships [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding Soft Erections: Causes, Impacts, and Strategies for Sexual Confidence [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Chronic Inflammation's Impact on Sexual Health: Mechanisms and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Overcoming Soft Erections: From Frustration to Fulfillment with Medical and Lifestyle Solutions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Innovative Devices and Holistic Approaches for Managing Soft Erections and ED [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Soft Erections: Understanding, Impact, and Building Intimacy in Relationships [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Cardiovascular Health's Impact on Erectile Function and Soft Erections in Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Alternative Medicine and Acupuncture for Enhancing Erectile Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Soft Erections: Lifestyle and Psychological Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Soft Erections: Understanding Causes, Preparing for Doctor Visits, and Exploring Treatments [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Mindfulness Techniques for Managing Soft Erections in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Soft Erections and Self-Esteem: Psychological Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Superfoods Boost Vascular Health, Enhance Erection Quality: Dark Chocolate, Walnuts, More [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Prostate Health and Soft Erections: Understanding and Managing the Connection [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Digital Health Tools for Managing Soft Erections in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Erectile Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Physical Therapy: A Promising Solution for Soft Erections and Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins and Their Impact on Male Sexual Health: Understanding Soft Erections [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Obesity and Soft Erections: Enhancing Sexual Health Through Weight Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Soft Erections: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- PDE5 Inhibitors: A Targeted Solution for Soft Erections and ED Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Innovative Technologies Transforming Erectile Dysfunction Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hormonal Balance: Key to Enhancing Erectile Strength in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Soft Erections in American Males: Impact of Anxiety, Depression, and Holistic Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nitric Oxide's Role in Enhancing Erections: Mechanisms and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Soft Erections: Causes, Mechanisms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Soft Erections: Causes, Treatments, and Breaking Stereotypes in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Soft Erections and Metabolic Syndrome: Causes, Implications, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sedentary Lifestyles and Erection Health: The Importance of Physical Activity [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic and Epigenetic Influences on Erectile Dysfunction: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Soft Erections vs. Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Impacts, and Treatments for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medications Causing Soft Erections: Causes, Identification, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Biofeedback: A Non-Invasive Solution for Enhancing Erectile Control in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Enhancing Sexual Stamina: Techniques for Managing Soft Erections in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Soft Erections: Impact on American Males' Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Cardiovascular Exercise Boosts Erection Quality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Stress Management Techniques to Improve Erectile Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Redefining Masculinity: Embracing Soft Erections and Enhancing Sexual Confidence [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Soft Erections: Causes, Therapies, and Surgical Options [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Soft Erections: Understanding, Impact, and Solutions for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Nerve Health's Crucial Role in Enhancing Erectile Function for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Innovative Research and Technologies Transforming Soft Erection Treatment [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Lifestyle Overhauls Boost Erection Quality: Diet, Exercise, and Health Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Cortisol's Impact on Erectile Dysfunction: Managing Stress for Better Sexual Health [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Breaking Barriers: Discussing Soft Erections and ED Among American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Natural Aphrodisiacs: Exploring Their Impact on Male Sexual Health and ED [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Holistic Strategies for Enhancing Male Sexual Performance and Erection Quality [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Soft Erections: Physical, Psychological, and Social Impacts on American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
Word Count: 618