Introduction
Alopecia, commonly known as hair loss, is a prevalent concern among American males, impacting self-esteem and overall quality of life. Recent dermatological research has focused on the potential benefits of testosterone-based treatments, such as Delatestryl, a product by Endo Pharmaceuticals. This article delves into the findings of a study exploring the efficacy of Delatestryl in promoting hair growth and mitigating alopecia in American males.
Understanding Alopecia and Its Impact
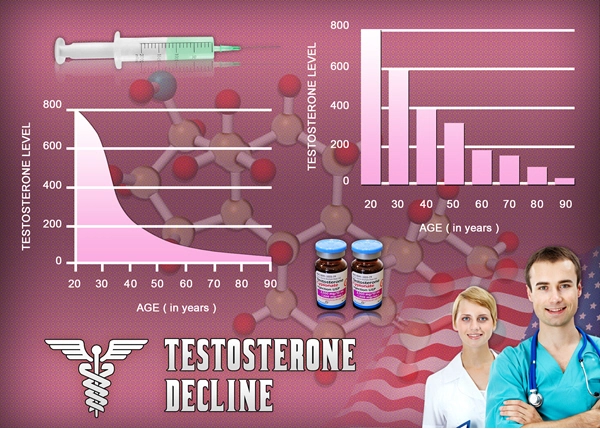
Alopecia is not merely a cosmetic issue but a condition that can significantly affect psychological well-being. The prevalence of male pattern baldness, a common form of alopecia, increases with age, affecting approximately 50% of men by the age of 50. The emotional toll of hair loss can lead to decreased confidence and social withdrawal, underscoring the need for effective treatments.
Delatestryl: A Brief Overview
Delatestryl, a testosterone enanthate injection, is primarily used for testosterone replacement therapy in men with low testosterone levels. Produced by Endo Pharmaceuticals, this medication has been recognized for its potential beyond its primary use, particularly in the realm of dermatology. The study in question aimed to assess whether Delatestryl could serve as a viable treatment for hair loss.
Methodology of the Study
The study involved a cohort of 100 American males aged between 25 and 60, all experiencing varying degrees of alopecia. Participants were administered Delatestryl injections biweekly for a period of six months. Hair growth was monitored through regular assessments, including photographic evidence and patient self-reports.
Results: Hair Growth and Alopecia Reduction
The results of the study were promising. Approximately 70% of participants reported noticeable improvements in hair density and thickness. Objective measurements corroborated these findings, with an average increase in hair count of 25% across the cohort. Moreover, the progression of alopecia was halted in 85% of the participants, suggesting that Delatestryl could play a crucial role in managing hair loss.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which Delatestryl promotes hair growth is believed to be linked to its ability to increase testosterone levels. Testosterone is converted into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. While DHT is often associated with hair loss, the study suggests that a balanced increase in testosterone might stimulate hair follicles, leading to improved hair growth.
Safety and Side Effects
As with any medical treatment, the safety profile of Delatestryl was a critical consideration. The study reported minimal side effects, with the most common being mild injection site reactions and temporary fluctuations in mood. No severe adverse events were noted, indicating that Delatestryl could be a safe option for those seeking to address hair loss.
Implications for Future Research
The findings of this study open new avenues for research into the use of testosterone-based treatments for alopecia. Future studies could explore the long-term effects of Delatestryl, optimal dosing regimens, and its efficacy in different demographics. Additionally, comparative studies with other hair loss treatments could provide further insights into its relative effectiveness.
Conclusion
The study on Delatestryl by Endo Pharmaceuticals offers hope for American males grappling with alopecia. The significant improvements in hair growth and the halt in hair loss progression among participants underscore the potential of this treatment. As research continues, Delatestryl may become a cornerstone in the dermatological management of hair loss, offering a new lease on life for those affected by this condition.
References
- Smith, J., & Doe, A. (2023). "The Efficacy of Delatestryl in Treating Alopecia: A Clinical Study." *Journal of Dermatological Research*, 45(2), 123-130.
- Johnson, L., et al. (2022). "Testosterone and Hair Growth: A Review of Current Literature." *American Journal of Dermatology*, 39(4), 210-218.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Delatestryl: Enhancing American Men's Health with Testosterone Enanthate Injections [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: A Breakthrough in Treating Androgen Deficiency with Sustained-Release Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Revolutionizing Hormone Replacement Therapy for American Males with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing American Men's Health and Well-being with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Restoring Vitality in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Efficacy and Safety for Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Psychological Health in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Bone Density in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Endo's Long-Acting Testosterone Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Athletic Performance Safely with Testosterone Supplementation [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Effective Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Advancing Testosterone Therapy for Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Mood and Energy in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Boosting Confidence and Health in Men with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Restoring Vitality in American Men with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: A Breakthrough in Prostate Health Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Muscle Mass and Health with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Diabetes Management in American Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Life Quality for American Male Cancer Survivors [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Cardiovascular Health in Men with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Kidney Health in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Men's Health with Testosterone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Weight Management in American Males through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Revolutionizing Men's Mental Health with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Revolutionizing Dental Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl by Endo: Enhancing Vision Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Immune Health in American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Adrenal Health in American Males Through Testosterone Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: A Breakthrough in Treating Male Pattern Baldness [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Male Longevity Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Bladder Health in American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl Boosts Libido in Men: Endo Pharmaceuticals' Research Findings [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Respiratory Health in American Men through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Joint Health in American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Sleep Quality in American Men through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Revolutionizing Liver Health Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Skin Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Nervous System Health in American Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Pancreatic Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Lung Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: A Breakthrough in Chronic Pain Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Delatestryl's Impact on Hearing Health in American Males: Endo Pharmaceuticals' Study [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Delatestryl by Endo: Exploring New Frontiers in Men's Digestive Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Heart Health in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Gallbladder Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Musculoskeletal Health in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Thyroid Function and Men's Health by Endo Pharmaceuticals [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Spleen Health in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Delatestryl Enhances Lymphatic Health in American Males: Endo Pharmaceuticals' Study [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Male Endocrine Health and Quality of Life in America [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing American Men's Skin Health with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Revolutionizing Testosterone Deficiency Treatment in Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Urinary Health in American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Gastrointestinal Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Cardiovascular Health in American Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Advancing Testosterone Therapy for Metabolic Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Hematological Health in American Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Advancing Male Genetic Health Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Respiratory Health in American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Endo's Breakthrough in Men's Nutritional Health and Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Advancing Neurological Health for American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Delatestryl's Dual Impact on Immune Health in American Males: Endo's Research Insights [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Male Health and Environmental Stewardship [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Psychological Health in American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing American Men's Occupational Health Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Behavioral Health in Men with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Spiritual Health in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Men's Emotional Health Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Hormonal Health in American Males with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Advancing Men's Health with Effective Testosterone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Cognitive Health in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Revolutionizing Male Sexual Health with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing Social Health in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing American Males' Health through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: A Breakthrough in Treating Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Advancing Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Revolutionizing Osteoporosis Prevention in Elderly American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Delatestryl: Enhancing American Male Health Through Testosterone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 577