Introduction
The use of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), such as Depo Testosterone Pfizer, has become increasingly common among American males seeking to address hypogonadism and other related conditions. While the benefits of TRT are well-documented, the long-term effects on various bodily systems, particularly the respiratory system, warrant further investigation. This article aims to explore the potential respiratory health implications of prolonged Depo Testosterone Pfizer use in American males, shedding light on an often-overlooked aspect of TRT.
Background on Depo Testosterone Pfizer
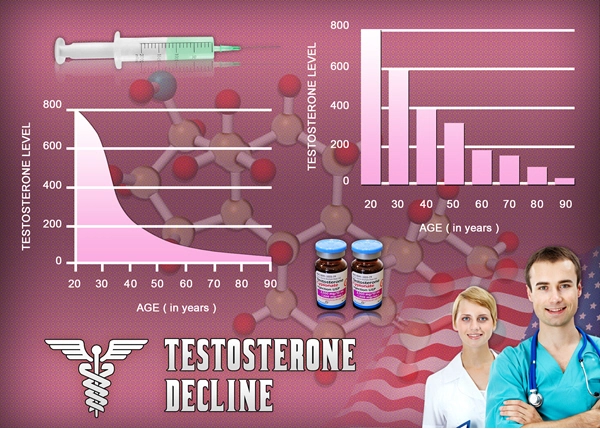
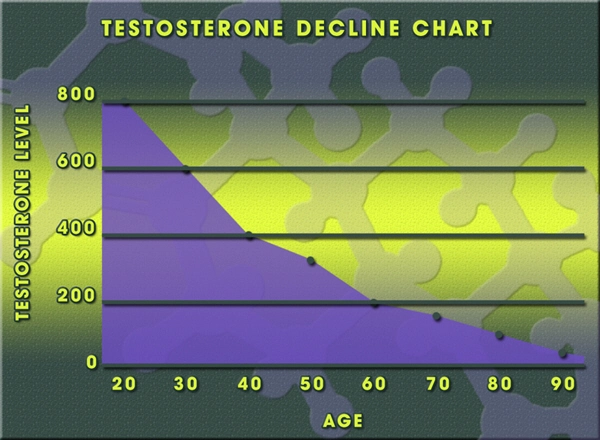
Depo Testosterone Pfizer is an injectable form of testosterone cypionate, a synthetic version of the primary male sex hormone. It is commonly prescribed to treat low testosterone levels in men, which can manifest as decreased libido, fatigue, and muscle loss. The drug is administered via intramuscular injection, typically every one to four weeks, depending on the patient's needs and response to treatment.
Respiratory Health and Testosterone
The relationship between testosterone levels and respiratory health is complex and not fully understood. Some studies suggest that testosterone may have a protective effect on the lungs, potentially reducing the risk of certain respiratory conditions. However, other research indicates that elevated testosterone levels could be associated with an increased risk of sleep apnea and other breathing disorders.
Investigating Long-Term Effects
To date, there have been limited studies specifically examining the long-term effects of Depo Testosterone Pfizer on respiratory health in American males. However, some research has investigated the impact of TRT on lung function and respiratory symptoms.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that men receiving TRT had a higher prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing compared to those not receiving treatment. Another study in the European Respiratory Journal suggested that long-term TRT use may be associated with a decline in lung function, as measured by forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1).
Potential Mechanisms
The exact mechanisms by which Depo Testosterone Pfizer may affect respiratory health are not fully elucidated. Some theories suggest that testosterone could influence the central respiratory control system, potentially leading to changes in breathing patterns. Additionally, testosterone may impact the structure and function of the upper airway, contributing to the development of sleep apnea.
Clinical Implications and Recommendations
Given the limited but concerning evidence regarding the potential respiratory effects of long-term Depo Testosterone Pfizer use, healthcare providers should carefully monitor patients receiving TRT for any signs of respiratory issues. Regular assessments of lung function and sleep quality may be warranted, particularly in patients with pre-existing respiratory conditions or risk factors.
Patients should be educated about the potential respiratory risks associated with long-term TRT use and encouraged to report any new or worsening respiratory symptoms to their healthcare provider promptly. In some cases, alternative forms of TRT or adjustments to the treatment regimen may be necessary to minimize potential respiratory side effects.
Future Research Directions
Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term respiratory effects of Depo Testosterone Pfizer in American males. Large-scale, longitudinal studies with robust methodology are essential to clarify the relationship between TRT and respiratory health. Additionally, investigations into the underlying mechanisms and potential risk factors for respiratory complications in TRT users could inform the development of targeted screening and management strategies.
Conclusion
While Depo Testosterone Pfizer can be an effective treatment for low testosterone levels in American males, the potential long-term effects on respiratory health cannot be overlooked. The limited evidence available suggests a possible association between prolonged TRT use and an increased risk of respiratory issues, including sleep-disordered breathing and declines in lung function. Healthcare providers and patients must be aware of these potential risks and take appropriate measures to monitor and manage respiratory health in men receiving TRT. As research in this area continues to evolve, a more comprehensive understanding of the respiratory implications of Depo Testosterone Pfizer use will emerge, guiding clinical practice and improving patient outcomes.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Sexual Health in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on Weight Management in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Psychological Impacts on Mood, Cognition, and Self-Esteem in Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- American Men's Experiences with Depo Testosterone Therapy: Benefits and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Energy and Vitality in Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Associated Risks in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on Prostate Health and Cancer Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Low Testosterone Treatment [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Vital for Men's Health, Challenges in Accessibility and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Efficacy and Safety in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Depo Testosterone: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Considerations for Transgender American Males' HRT [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Treating Delayed Puberty in American Males Effectively [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Skin Health Effects in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Therapy: Future Trends and Impact on American Male Health [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Libido and Sexual Function in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for ED in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects on Blood Sugar Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits vs. Cardiovascular Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Monitoring, Dosage Adjustment, and Safety for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo-Testosterone's Impact on Sleep Quality in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Risks for Older American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life for American Male Cancer Survivors [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Chronic Conditions in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing American Male Body Composition and Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Stress Management in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Vital Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Male Adolescents [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life Quality in American Male Veterans [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Endurance in American Male Athletes - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone and Hair Loss: Risks, Management, and Psychological Impact [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Pfizer: Enhancing Mood and Well-being in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Digestive Health in American Males: Effects and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Immune System: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Males with TRT [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Adjunct in Diabetes Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Balancing Hormone Therapy and Fertility in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits for Hypogonadism and Potential Eye Health Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life Quality for American Males with HIV/AIDS [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits, Liver Risks, and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Joint Health in American Males: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Fertility in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Pfizer's Injectable HRT for American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Risks for American Male Weightlifters [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Treating Anemia in American Men with Pfizer's Injectable Solution [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects on Kidney Function and Monitoring in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Treating Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Role in Managing Osteoporosis in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Ear Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Potential Treatment for Anxiety in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Thyroid Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Autoimmune Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Solution for Migraine Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: Benefits and Side Effects [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Uses, Allergic Reactions, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Insomnia in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Option for Chronic Pain Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits for Neurological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Understanding TRT for Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Respiratory Health in Hypogonadal American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Arthritis Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects, Risks, and Management in Male Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Psychiatric Disorders in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Considerations for American Males with Genetic Disorders [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Potential Dermatological Uses and Considerations in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Metabolic Health in American Males with Pfizer's Therapy [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life for American Males with Renal Disorders [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo-Testosterone's Impact on Urological Disorders in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Inflammatory Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Hematological Disorders in American Males: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Role in Managing Infectious Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Enhances Body Composition and Muscle Mass in Hypogonadal Men: Clinical Trial [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effective Hypogonadism Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]
Word Count: 639