Introduction
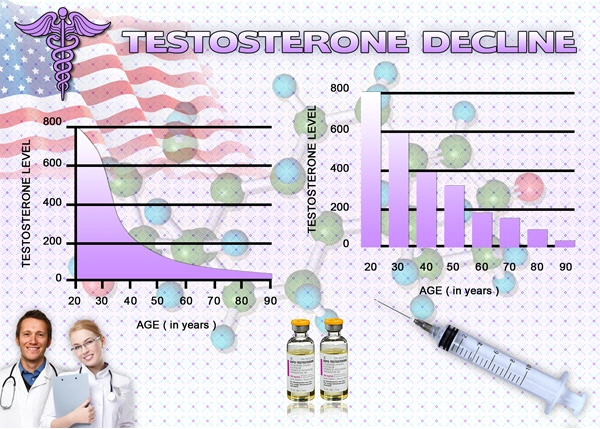
Alzheimer's disease represents a significant public health challenge, particularly among American males, where cognitive decline can severely impact quality of life. Recent research has begun to explore the potential neuroprotective effects of testosterone enanthate, a long-acting form of testosterone, on cognitive function in this demographic. This article delves into the findings of a neurological study that investigates the influence of testosterone enanthate on cognitive decline in American males diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease.
Understanding Testosterone Enanthate
Testosterone enanthate is a synthetic derivative of testosterone, commonly used in hormone replacement therapy to treat low testosterone levels in men. Its long-acting nature, with effects lasting up to two weeks, makes it a practical choice for clinical studies. Beyond its traditional use, emerging research suggests that testosterone may play a role in brain health, potentially offering benefits in neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer's disease.
The Study Design
The study in question was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted over 12 months. It involved 150 American males aged 60 to 80 years, all diagnosed with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Participants were divided into two groups: one receiving weekly intramuscular injections of testosterone enanthate and the other receiving a placebo. Cognitive function was assessed using standardized tests at baseline, 6 months, and 12 months.
Cognitive Outcomes
The results of the study were promising. Participants receiving testosterone enanthate showed a statistically significant improvement in cognitive function compared to the placebo group. Specifically, improvements were noted in memory recall, attention, and executive function. These findings suggest that testosterone enanthate may help slow the progression of cognitive decline in American males with Alzheimer's disease.
Mechanisms of Action
The neuroprotective effects of testosterone enanthate may be attributed to several mechanisms. Testosterone is known to influence neuronal health by promoting neurogenesis, enhancing synaptic plasticity, and reducing neuroinflammation. Additionally, it may improve cerebral blood flow, which is crucial for maintaining cognitive function. These multifaceted actions could collectively contribute to the observed benefits in cognitive performance among study participants.
Safety and Tolerability
Safety data from the study indicated that testosterone enanthate was well-tolerated, with no serious adverse events reported. Common side effects included mild injection site reactions and transient increases in hematocrit levels, which were managed with routine monitoring. These findings support the feasibility of using testosterone enanthate as a therapeutic option for cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The study's outcomes have significant implications for clinical practice, particularly in the management of Alzheimer's disease in American males. Given the potential to slow cognitive decline, healthcare providers may consider testosterone enanthate as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. However, further research is needed to confirm these findings and to establish optimal dosing and long-term safety profiles.
Future Research Directions
Future studies should aim to replicate these findings in larger, more diverse cohorts and explore the long-term effects of testosterone enanthate on cognitive function. Additionally, research should investigate the potential benefits of combining testosterone therapy with other Alzheimer's treatments to maximize cognitive outcomes. Understanding the precise mechanisms by which testosterone exerts its neuroprotective effects will also be crucial for developing targeted therapies.
Conclusion
The study on testosterone enanthate and its influence on cognitive decline in American males with Alzheimer's disease offers hope for a novel therapeutic approach. By demonstrating significant improvements in cognitive function, this research underscores the potential of testosterone enanthate as a neuroprotective agent. As the scientific community continues to unravel the complexities of Alzheimer's disease, such findings pave the way for more effective and personalized treatments, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for affected individuals.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Associated Risks in the US [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Long-Term Health Risks of Testosterone Enanthate Use in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Low Testosterone Treatment [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Sleep Quality in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Dispelling Myths and Understanding Facts for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Cognitive Function in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Prostate Risks, and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Cycle: Enhancing Performance and Managing Risks in Athletes [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Personalization, Monitoring, and Lifestyle Integration for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Blood Sugar Levels in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Withdrawal: Symptoms and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Male Fertility: Insights for American Patients [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Obesity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Ethical Dilemmas of Testosterone Enanthate Use Among American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Enhancing Veteran Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Effects on Hair Growth and Loss in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Appetite and Digestion in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential New Treatment for Allergies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Injury Recovery in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Joint Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Anemia in Hypogonadal American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Endurance in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Cultural Perceptions and Masculinity in American Society [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Combating Age-Related Decline in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Solution for Muscle Wasting in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Process, and Risks for Men Over 50 [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Stress Management Tool for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Skin Elasticity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Treatment for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Endurance in American Male Athletes - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Limitations, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat, Boosting Performance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: Risks and Recommendations [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Vision and Eye Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Costs, and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Dosage, Monitoring, and Lifestyle for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Impacts on Life Expectancy and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Post-Surgical Recovery in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Respiratory Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Autoimmune Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Role in Managing Diabetes in American Men: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Kidney Function Impact in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Hearing Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Liver Health in American Men: Risks and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Hypertension in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Male Reproductive Health and Fertility in America [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Treatment for Gastrointestinal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Neurological Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Adrenal Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle and Bone Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Thyroid Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Endocrine Impact in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Respiratory Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Males: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Emerging Role in Dermatology for American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Hematological Health in American Men: Benefits and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Metabolic Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Neurological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Metabolic Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: An Analysis [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Potential Benefits for Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Impacts and Management of Reproductive Health in Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Key Role in Treating Hypogonadism and Enhancing Male Health [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Potential Treatment for Hematological Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Gastrointestinal Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Neurological Impact on American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Effective Management of Low T in American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 582