Introduction
The advent of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, such as Viagra (sildenafil citrate), has revolutionized the management of erectile dysfunction (ED). This study aims to explore the association between Viagra usage and various lifestyle factors among American males, providing insights that may guide clinical practice and public health initiatives.
Methodology
A cross-sectional study was conducted using a structured questionnaire distributed to a cohort of 1,500 American males aged 40-70 years. Participants were asked about their Viagra usage, frequency, and the presence of lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, and dietary habits. Data were analyzed using logistic regression models to identify significant associations.
Prevalence of Viagra Usage
Our findings indicate that 22% of the surveyed population reported using Viagra at least once in the past year. This prevalence aligns with previous studies suggesting that ED is a common concern among middle-aged and older American men. The usage rate underscores the importance of understanding the factors that influence the decision to use ED medication.
Association with Smoking
A significant association was observed between Viagra usage and smoking status. Current smokers were 1.7 times more likely to use Viagra compared to non-smokers (p<0.05). This finding supports the existing literature that links smoking with a higher risk of ED, likely due to its detrimental effects on vascular health.
Alcohol Consumption and Viagra Use
Moderate to heavy alcohol consumption was also found to be a significant predictor of Viagra usage. Men who reported consuming more than 14 alcoholic drinks per week were 1.5 times more likely to use Viagra (p<0.05). This association may reflect the impact of alcohol on sexual performance and the subsequent need for pharmacological intervention.
Physical Activity Levels
Interestingly, our data revealed an inverse relationship between physical activity and Viagra usage. Men who engaged in regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week) were less likely to use Viagra (OR=0.8, p<0.05). This suggests that an active lifestyle may help mitigate the risk of ED.
Dietary Habits and ED Medication
Dietary habits also emerged as a significant factor. Participants who reported a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains were less likely to use Viagra (OR=0.7, p<0.05). Conversely, those with a diet high in processed foods and sugars showed a higher likelihood of using ED medication (OR=1.3, p<0.05). These findings highlight the potential role of diet in the prevention and management of ED.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors, such as stress and anxiety, were also assessed. Men reporting high levels of stress were 1.4 times more likely to use Viagra (p<0.05). This association underscores the importance of addressing mental health in the context of ED management.
Clinical Implications
The results of this study have several clinical implications. Healthcare providers should consider lifestyle factors when discussing ED management with patients. Encouraging smoking cessation, moderating alcohol consumption, promoting physical activity, and advocating for a healthy diet may reduce the need for ED medication. Additionally, addressing psychological factors such as stress and anxiety may enhance treatment outcomes.
Public Health Considerations
From a public health perspective, these findings suggest the need for targeted interventions to promote healthier lifestyles among American males. Public health campaigns could focus on the benefits of a healthy diet and regular exercise in preventing ED, thereby reducing the reliance on medications like Viagra.
Limitations and Future Research
While this study provides valuable insights, it is not without limitations. The cross-sectional design limits our ability to infer causality. Future longitudinal studies are needed to better understand the temporal relationship between lifestyle factors and Viagra usage. Additionally, the self-reported nature of the data may introduce bias, necessitating further research with objective measures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study highlights significant associations between Viagra usage and various lifestyle factors among American males. Smoking, alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, poor diet, and psychological stress are all linked to an increased likelihood of using ED medication. These findings emphasize the importance of a holistic approach to ED management, integrating lifestyle modifications with pharmacological interventions. By addressing these modifiable risk factors, healthcare providers and public health officials can work together to improve the sexual health and overall well-being of American men.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Comparing Viagra, Levitra, and Cialis: Effective ED Treatments for American Men [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2025]
- Revolutionizing ED Care: Exploring Advanced Treatments Beyond Traditional Medications [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2025]
- Decoding the History of Sildenafil: A Groundbreaking Revolution in Treating Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Decoding Sildenafil: The Pillar of Viagra's Unprecedented Success [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Comparative Analysis: Viagra And Generic Sildenafil [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Decoding the Power Pill: A Comprehensive Exploration of Viagra's Mechanism [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Unfolding the Odyssey of Erectile Dysfunction Treatments: A Chronological Insight from Viagra to Contemporary Remedies [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Demystifying the Biochemical Pathways of Sildenafil: The Engine Behind Viagra's Potency [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Underscoring the Role of Viagra in Cardiovascular Health: An In-depth Examination of Benefits and Potential Risks [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Optimizing Sildenafil Dosage for Erectile Dysfunction: Guidelines, Adjustments, and Safety Considerations [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Understanding Viagra: Side Effects and Safety for American Men [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Diet on Viagra Efficacy: Foods to Embrace and Avoid [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Managing Side Effects of Viagra for Effective Erectile Dysfunction Treatment [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Exploring Viagra's Role in Treating Erectile Dysfunction and Hypertension [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Impact of Age on Viagra's Efficacy: Insights for American Men Seeking ED Treatment [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- The Interplay of Viagra and Diabetes: Efficacy, Safety, and Management Insights [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Exploring Viagra's Psychological Impact on Self-Esteem in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- The Evolution of Male Sexual Health: The Impact of Viagra on Culture and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Life-Changing Impact of Viagra: Real Stories from American Men [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Impact of Lifestyle on Viagra's Effectiveness in American Males [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Viagra and Libido: Understanding the Impact and Dispelling Myths for American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Viagra and Alcohol: Safety, Effects, and Guidelines for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Viagra's Recreational Use: Risks, Rewards, and Health Impacts in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Placebo Effect in Viagra: Psychological Impact on American Males' ED Treatment [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Viagra's Impact on U.S. Market and Health Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Generic Sildenafil: Revolutionizing ED Treatment with Affordability and Accessibility [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Sildenafil: From Angina Drug to ED Treatment Revolutionizing American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Viagra: Uses, Drug Interactions, and Safety Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Viagra: Debunking Myths and Clarifying Facts for American Men's Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Global Viagra Pricing: Factors, Comparisons, and U.S. Cost Navigation for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Safeguarding Health: Identifying and Avoiding Counterfeit Viagra for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Viagra's Role in Managing Pulmonary Hypertension in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Viagra Usage Guide: Dos, Don'ts, and Safety Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Viagra's Impact on Mental Health: Enhancing Well-being in American Men with ED [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Viagra's Impact: Transforming ED Treatment and Social Attitudes in America [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Viagra and Exercise: Synergistic Effects on Sexual Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Viagra: Enhancing Sexual Confidence and Transforming ED Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Stress-Induced ED in American Males: Understanding and Treating with Viagra [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Sildenafil vs. Other Oral ED Medications: Efficacy, Onset, and Safety for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Viagra's Impact on Prostate Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Sildenafil's Versatile Therapeutic Uses in American Males Beyond Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Viagra: Enhancing Sexual Performance and Quality of Life in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Viagra: Enhancing Blood Flow for American Males with ED [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Sildenafil's Off-Label Uses: Benefits for American Males Beyond Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Viagra in Pop Culture: Iconic References and Impact on Male Health Perceptions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Smoking Reduces Viagra Efficacy: Quit for Better ED Treatment Outcomes [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Navigating Viagra's Legal Landscape: Regulations and Policies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Generic Sildenafil: Revolutionizing ED Treatment with Affordable, Effective Options [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sildenafil's Impact on Urology: From ED to Broader Applications in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Cultural Attitudes Shaping Viagra Use Among American Males: Masculinity, Media, and Generational Views [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Viagra: Enhancing Sexual Function and Its Potential Impact on Hormonal Health in Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Navigating Viagra Discussions with Doctors: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Viagra: Revolutionizing Erectile Dysfunction Treatment and Men's Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sildenafil: Understanding Its Role in Treating Erectile Dysfunction and Beyond [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Viagra's Role in Sexual Rehabilitation for American Males Post-Surgery [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Viagra: From ED Treatment to Recreational Use Debate Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Viagra and Privacy: Navigating ED Treatment and Data Security in the Digital Age [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Viagra's Economic Impact: Revolutionizing ED Treatment and Pharmaceutical Market Dynamics [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Viagra: Revolutionizing Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Viagra and Male Fertility: Dispelling Myths and Clarifying Facts for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Viagra Treatment, and Lifestyle Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Viagra: Revolutionizing ED Treatment and Sexual Health in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Viagra's Impact on American Couples' Intimacy and Relationship Dynamics [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Maximizing Viagra Benefits: Timing, Dosage, Lifestyle for Enhanced Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Viagra's Impact on ED: Ethical Marketing and Public Health Concerns in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Viagra: Understanding Use, Effects, and Integration into Health Routine [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Sildenafil Contraindications: Essential Guide for Safe Usage in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Telemedicine Revolutionizes ED Management with Viagra for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Viagra's Journey: From Discovery to FDA Approval and Impact on ED Treatment [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
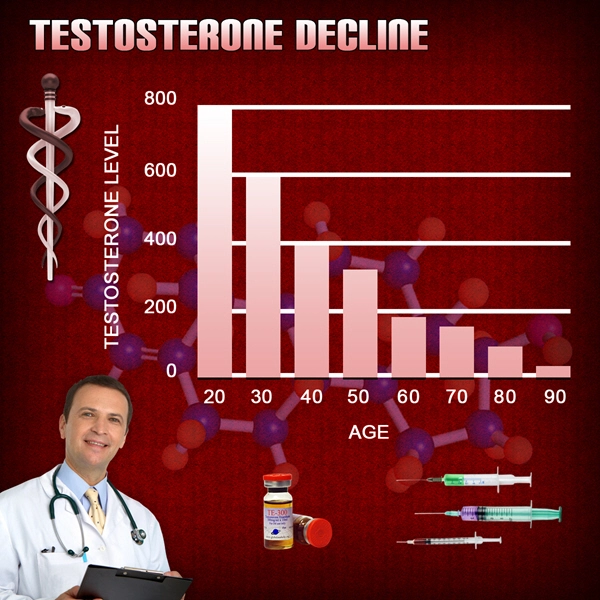
- Testosterone Levels and Viagra Efficacy in American Men: Optimizing ED Treatment [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Viagra vs. Natural Remedies for ED: Efficacy, Safety, and Cost Compared [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Viagra: Enhancing Sexual Satisfaction and Relationship Dynamics in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Long-Term Viagra Use: Benefits, Risks, and Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Viagra Use in Men with Chronic Illnesses: Safety, Interactions, and Management [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Sildenafil: Restoring Sexual Function in American Men Post-Injury [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Sildenafil Pharmacokinetics: Optimizing ED Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Viagra's Role in Treating Erectile Dysfunction Among Younger American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Viagra Interactions: Safety and Efficacy for American Males with ED [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Viagra vs. Other ED Treatments: Clinical Outcomes and Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Erectile Dysfunction: Sildenafil vs. Lifestyle Changes - A Comparative Analysis [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
Word Count: 189