Introduction
Sleep is a fundamental physiological process that significantly impacts overall health and well-being. In American men, sleep deprivation has become increasingly prevalent, contributing to a myriad of health concerns. This article delves into the intricate relationship between sleep and endocrinology, specifically focusing on how sleep deprivation affects hormonal balance and overall health in American men.
The Physiology of Sleep and Hormonal Regulation
Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating various hormonal systems within the body. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which governs the stress response, and the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, responsible for reproductive function, are particularly sensitive to sleep patterns. During sleep, the body undergoes essential processes such as the release of growth hormone, which is vital for muscle growth, tissue repair, and metabolism. Furthermore, sleep influences the secretion of cortisol, a key stress hormone, and testosterone, a critical male sex hormone.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Hormonal Balance
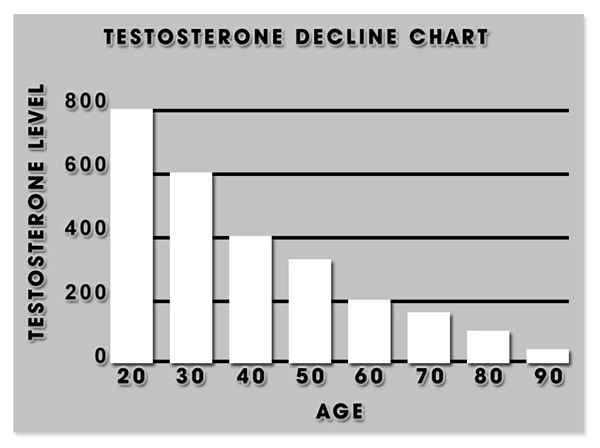
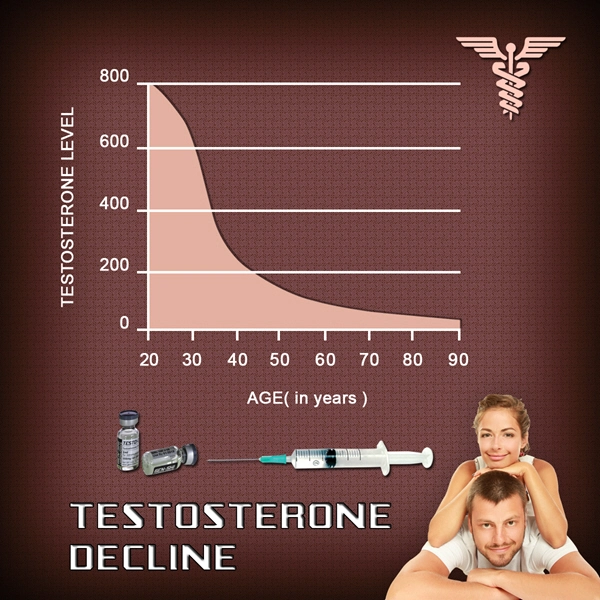
Sleep deprivation disrupts the delicate balance of hormones in American men, leading to a cascade of physiological consequences. Studies have shown that insufficient sleep can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which, when chronically high, can contribute to insulin resistance, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. Moreover, sleep deprivation has been linked to decreased testosterone levels, which can adversely affect libido, muscle mass, and overall vitality.
Sleep Deprivation and Metabolic Health
One of the most significant impacts of sleep deprivation on American men is its effect on metabolic health. Lack of sleep has been associated with increased appetite and cravings for high-calorie foods, primarily due to alterations in the hormones ghrelin and leptin. Ghrelin, known as the "hunger hormone," increases with sleep deprivation, while leptin, the satiety hormone, decreases. This imbalance can lead to overeating and weight gain, exacerbating the risk of developing metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.
Cardiovascular Implications of Sleep Deprivation
The cardiovascular system is not immune to the effects of sleep deprivation. Chronic sleep loss has been linked to hypertension, increased inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction, all of which are risk factors for heart disease. In American men, who already face a higher risk of cardiovascular issues, sleep deprivation can significantly compound these risks, making it imperative to prioritize adequate sleep for heart health.
Psychological and Cognitive Effects
Beyond its physical impacts, sleep deprivation also affects the psychological and cognitive health of American men. Insufficient sleep can lead to mood disturbances, increased irritability, and a higher susceptibility to mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. Cognitively, sleep deprivation impairs attention, memory consolidation, and decision-making abilities, which can have profound effects on daily functioning and overall quality of life.
Strategies for Improving Sleep Quality
To mitigate the adverse effects of sleep deprivation on hormonal balance and overall health, American men can adopt several strategies to improve sleep quality. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a sleep-conducive environment, and practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing can significantly enhance sleep quality. Additionally, limiting exposure to blue light from screens before bedtime and avoiding caffeine and heavy meals in the evening can further support healthy sleep patterns.
Conclusion
The impact of sleep deprivation on endocrinology and overall health in American men cannot be overstated. By understanding the intricate relationship between sleep and hormonal balance, men can take proactive steps to prioritize sleep and safeguard their health. Addressing sleep deprivation not only improves hormonal regulation but also enhances metabolic, cardiovascular, psychological, and cognitive well-being, ultimately contributing to a healthier and more vibrant life.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Clomiphene Citrate Therapy in Men: Enhancing Endocrine Function in Secondary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2025]
- Comprehensive Endocrine Evaluation Essential for Diagnosing Fatigue in American Men [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Exploring hCG Monotherapy and Exogenous Testosterone in Young Men with Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: A Focus on Testicular Function [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- The Crucial Link Between Insulin Resistance and Male Hormonal Imbalances: Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- The Crucial Link: Vitamin D's Impact on Androgen Metabolism and Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- The Critical Balance: Cortisol and Testosterone's Impact on Men's Health and Hormones [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Exploring Neurosteroid Modulation as a Pioneering Treatment for Stress-Induced Endocrine Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) in Male Endocrine Disorders [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Exploring the Role of Oxytocin in Male Endocrinology: From Physiology to Therapeutic Potential [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Precision Medicine Revolutionizes HRT for Male Endocrine Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Impact on Male Health and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Adipokines and Male Endocrine Health: Mechanisms, Impacts, and Therapeutic Prospects [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Chronobiology's Role in Male Hormone Secretion and Endocrinology for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Trace Elements' Impact on Hormone Metabolism in American Men: Zinc, Selenium, Magnesium [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Gut Microbiome's Role in Men's Steroid Hormone Metabolism and Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Thyroid-Testicular Axis: Impact on Male Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Somatostatin Analogues: Versatile Applications in Male Endocrinology and Beyond [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Inflammaging and Male Hormonal Health: Strategies for Endocrine Optimization [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Mitochondrial Health and Male Hormones: Therapeutic Targets for Age-Related Decline [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Metabolomics Revolutionizing Male Endocrine Health Diagnostics and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- OSA in American Men: Exploring Endocrine Effects Beyond Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Ghrelin Modulation Enhances Weight Management in Hypogonadal American Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Energy Balance and Reproductive Function in American Men: Neuroendocrine Integration and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- NAFLD's Impact on Male Endocrine and Reproductive Health: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Male Hormonal Health and Cognitive Function: The Impact of Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Pharmacogenomics Revolutionizes Hormone Therapy in Men: Tailoring Treatment to Genetic Profiles [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- SHBG's Role in Male Hormonal Health: Regulation, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Implications [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Luteinizing Hormone Dynamics: Diagnosis and Treatment in Male Endocrinology [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Polycythemia in Men on Testosterone Therapy: Monitoring and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormone Optimization and Lifestyle Strategies to Combat Sarcopenia in Aging Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Epigenetic Changes from HRT in American Men: Longitudinal Insights and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Leptin Resistance in American Men: Endocrine Effects and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine Reserve Testing: Diagnosis and Management of Hormonal Imbalances in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Optimizing Bone Health: BMD Monitoring Protocols for Men on HRT in the USA [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Male Climacteric Syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Multidisciplinary Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise and Endocrinology in Men: Hormonal Dynamics and HRT Implications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Navigating Prostate Health During Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Risks and Monitoring Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Pituitary Incidentalomas in Men: Evaluation, Management, and Long-term Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Biomarkers in Male Endocrinology: Growth Factors and Cytokines' Clinical Applications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Androgen Receptor Sensitivity: Enhancing Personalized Hormone Therapy in Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Vasopressin's Therapeutic Roles in Male Endocrinology and Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing HPT Axis Recovery in American Men Post-Testosterone Therapy: Endocrinological Approaches [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Diurnal Hormone Patterns: Optimizing Endocrinology for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Post-Traumatic Hypopituitarism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrine Sequelae in Male TBI Patients: Long-Term Management and Follow-Up Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- ECS's Role in Male Reproductive Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Subclinical Endocrinopathies in Men: Diagnosis, Thresholds, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Inhibin B: Key Biomarker for Assessing Male Fertility and Endocrine Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Aging Men's Endocrine Changes: Impacts on Fertility and Offspring Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Opioid-Induced Endocrinopathy in Men: Mechanisms, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Multimarker Approach to Cardiometabolic Risk in Men on Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Endocrine Frailty in Aging Men: Hormonal Decline and Multimodal Intervention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Male Sex Hormones and Autoimmune Disease Management in American Men: Endocrinology Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- HRT and Telomere Length: Implications for Aging and Longevity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- INSL3: A Stable Biomarker for Leydig Cell Function in Male Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Neuropeptide Y: Key Regulator in Male Endocrine and Metabolic Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bioavailable Hormones: Key to Effective Male Endocrinology Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disruption in Men Post-Chemotherapy: Strategies and Support [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Male Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Counseling [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- AMH's Emerging Role in Adult Male Endocrinology and Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hyperparathyroidism's Impact on Male Reproductive Health: Diagnosis and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Radiation-Induced Hypopituitarism in Men: Diagnosis, Hormone Deficiency Patterns, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Hemochromatosis in American Men: Endocrine Effects, Screening, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- CKD's Impact on Male Endocrine Function: Adaptations and Therapeutic Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Male Sexual Desire Disorders: Endocrine Focus and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Osteoporosis in Men: Endocrine Evaluation, Hormone Therapy, and Dietary Management [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Adrenal Incidentalomas in Men: Evaluation, Management, and Long-term Follow-up Strategies [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Cushing's Syndrome in Men: Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Their Impact on Male Stress Urinary Incontinence [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Male Fertility Through Endocrinology [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Enhancing Endocrine Resilience in American Men: Strategies and Biological Insights [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Growth Hormone and IGF-1: Enhancing Male Athletic Performance and Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Endocrine Management of Hormone Therapy for Transgender Men: Protocols and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Androgen Action: Mechanisms, Prostate Health, and Targeted Therapies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Advancements in Male Hormonal Contraception: Impact and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- AI-Driven Precision Endocrinology: Personalizing Hormone Therapy for Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Enhancing Male Endocrinology Care with Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Quality Indicators in Male Endocrine Care: Development, Implementation, and Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Integrative Endocrinology: Holistic Hormone Therapy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Wearable Tech Revolutionizes Hormone Monitoring and HRT for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
Word Count: 571