Introduction
Arthritis, a common yet debilitating condition, affects millions of American males, significantly impacting their quality of life. While the role of genetics and lifestyle in arthritis is well-documented, the influence of endocrinology, particularly hormonal fluctuations, remains an area of growing interest and research. This article delves into the intricate relationship between endocrinology and joint health, exploring how hormonal imbalances can exacerbate or mitigate arthritis in American males.
The Role of Hormones in Joint Health
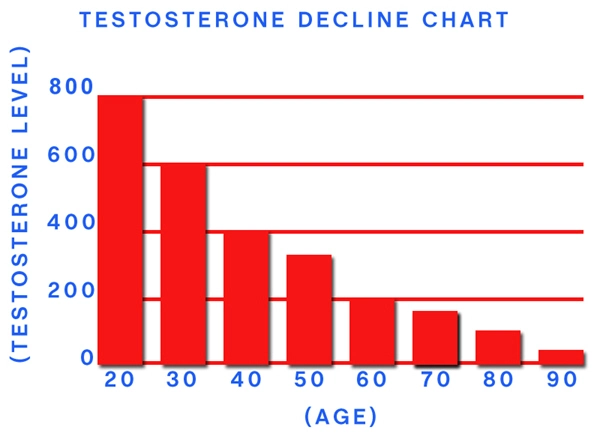
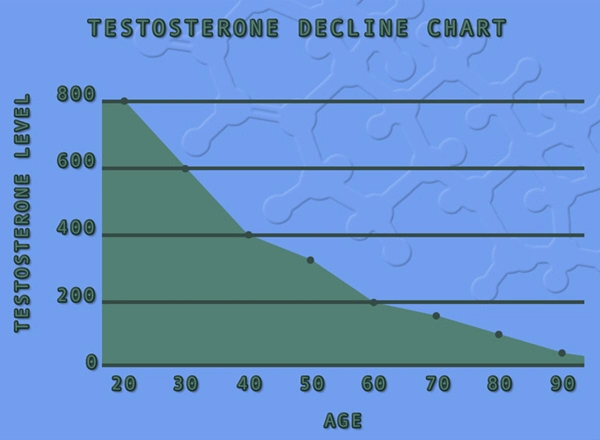
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including the maintenance of joint health. Key hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol have been identified as significant players in the development and progression of arthritis. Testosterone, traditionally considered a male hormone, has anti-inflammatory properties that can protect joints. Conversely, a decline in testosterone levels, often seen in aging males, may contribute to the onset of arthritis.
Estrogen, while more commonly associated with females, also influences joint health in males. Studies have shown that estrogen can modulate the immune response and inflammation, factors critical in the pathogenesis of arthritis. A balanced level of estrogen is essential for maintaining joint integrity and preventing the degradation of cartilage.
Cortisol, a stress hormone, can have a dual effect on joint health. While it is used therapeutically to reduce inflammation in arthritis, chronic elevation of cortisol levels can lead to joint damage and exacerbate arthritic symptoms. Understanding the delicate balance of these hormones is vital for managing arthritis effectively.
Hormonal Imbalances and Arthritis
Hormonal imbalances are a significant concern for American males, particularly as they age. Hypogonadism, characterized by low testosterone levels, is increasingly prevalent and has been linked to higher incidences of arthritis. The reduction in testosterone can lead to increased inflammation and joint pain, making it a critical factor to consider in the management of arthritis.
Moreover, the metabolic syndrome, often accompanied by hormonal dysregulation, can further complicate arthritis. Insulin resistance, a hallmark of metabolic syndrome, can lead to increased inflammation and joint deterioration. Addressing these hormonal imbalances through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can be pivotal in mitigating the progression of arthritis.
Therapeutic Approaches and Hormonal Regulation
The management of arthritis in American males often involves a multifaceted approach, with hormonal regulation playing a key role. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), particularly testosterone replacement, has shown promise in alleviating arthritic symptoms. By restoring testosterone levels, HRT can reduce inflammation and improve joint function.
Additionally, lifestyle interventions such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can help regulate hormone levels and improve overall joint health. Exercise, in particular, can stimulate the production of endorphins and other hormones that have anti-inflammatory effects, thus benefiting those with arthritis.
Future Directions in Research
The field of endocrinology and its impact on arthritis is ripe for further exploration. Ongoing research aims to better understand the specific mechanisms by which hormones influence joint health and to develop targeted therapies that can modulate these hormonal pathways. Advances in personalized medicine may soon allow for tailored hormonal treatments that address the unique needs of each individual with arthritis.
Conclusion
The interplay between endocrinology and joint health is a critical consideration for American males battling arthritis. By recognizing the role of hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol, and addressing hormonal imbalances through therapeutic and lifestyle interventions, significant strides can be made in managing and potentially preventing arthritis. As research continues to unravel the complexities of this relationship, the future holds promise for more effective and personalized treatments for arthritis in American males.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Hormonal Imbalances and Sleep Disorders: Impact on American Men's Health and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Crucial Role in Endocrine Health for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Role in Managing Chronic Fatigue in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies for Enhancing Endocrine Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Impact on Weight Management for American Males: Hormones and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hormonal Changes in Aging American Men: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Cancer Risk in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Endocrine Disorders in Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- PCOS in Transgender Men: Diagnosis, Management, and Holistic Care Approaches [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disruptors: Impact on American Male Health and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Lifestyle Impacts on Endocrine Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hormonal Optimization in Sports: Enhancing Performance Ethically for American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Male Infertility and Endocrinology: Understanding Hormonal Impacts on Fertility [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Gout in American Males: Endocrine Influences and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Impact on Sexual Health in American Males: Hormones, Dysfunction, and Holistic Care [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Kidney Health: Critical Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Mental Well-being: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Endocrine System in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Joint Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hormonal Impacts on Men's Immune Health in the U.S.: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine-Neurological Interplay in American Men: Diagnosis, Management, and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Their Role in Managing Male Depression in America [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men with Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormonal Dynamics and Skin Health in American Men: Androgens, Acne, Aging, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Prostate Cancer: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders and Heart Disease in American Men: Strategies and Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise Impacts on Endocrine Function in American Males: Hormonal Health Benefits [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders in Men: Impact on Skin Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Type 2 Diabetes in American Men: Endocrine Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine System and Liver Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine and Gastrointestinal Health Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Muscle Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health's Impact on Respiratory Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exploring ADHD and Endocrinology: Hormonal Imbalances and New Treatment Avenues [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring Endocrinological Interventions for PTSD in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Role in Managing Insomnia Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Vital Role in Treating Male Eating Disorders in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Stress Impact on Male Endocrine Health: Hormones and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Endocrine Health in American Men: Testosterone, Thyroid, and More [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Hearing Loss in American Males: Causes and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Foot Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Caffeine's Impact on Endocrine Health in American Males: Cortisol, Insulin, Testosterone, Thyroid [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Vision: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hormonal Fluctuations and Oral Health in American Men: Insights and Recommendations [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hormonal Hair Loss in American Men: Causes, Treatments, and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Male Anxiety: Endocrinological Insights and Treatments in the USA [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Sleep's Impact on Endocrine Health: Key Hormones and Practical Sleep Improvement Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Endocrine System's Impact on Digestive Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Impact on Endocrine Health in American Males: Key Nutrients and Diets [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Nail Changes in American Males: A Vital Connection [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Endocrinological Approaches Enhance Bipolar Disorder Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Eye Health: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Hand Conditions in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Ear Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hormonal Fluctuations and Nasal Health in American Men: Symptoms and Management [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hydration's Crucial Role in Endocrine Health for American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Throat Conditions in American Males: Hormonal Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Schizophrenia in Males: The Role of Endocrinology in Treatment and Management [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men with Lung Conditions: An Endocrinological Approach [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Dietary Supplements' Impact on Endocrine Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormonal Balance and Heart Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Exploring Hormonal Influences on Autism in American Males: Endocrine Insights and Therapies [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Endocrine System's Impact on Blood Health in American Males: Hormones, Disorders, and Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Mental Health's Impact on Endocrine Function in American Males: An Integrated Approach [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Exploring Endocrine Approaches to Treating OCD in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Endocrine and Nerve Health in American Males: Hormones, Disorders, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men with Kidney Disease: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hormonal Balance and Brain Health in American Men: Endocrinology Insights [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Skin Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in Men with Muscle Conditions: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Exploring Endocrine Therapy for Managing ADD Symptoms in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Crucial Role in Treating Male Eating Disorders in the USA [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Heart Health: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Choices Impact Endocrine Health in American Males: Diet, Exercise, Stress, Sleep, Substance Abuse [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Aging and Endocrine Function in American Males: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Liver Function: Impacts on American Males' Wellness [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Bone Health in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health's Impact on Joint Function in American Males: Hormonal Connections [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Impact on Male Health: Hormones, Aging, and Wellness [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Thyroid Health in American Men: Understanding Disorders, Symptoms, and Management [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 580