Introduction
Infertility affects a significant portion of the American male population, with hormonal imbalances playing a pivotal role in many cases. This article delves into the intricate relationship between endocrinology and male infertility, shedding light on the hormonal causes and exploring the latest treatment options available to affected individuals. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and embracing cutting-edge interventions, American males can navigate the challenging landscape of infertility with greater hope and informed decision-making.
The Hormonal Landscape of Male Infertility
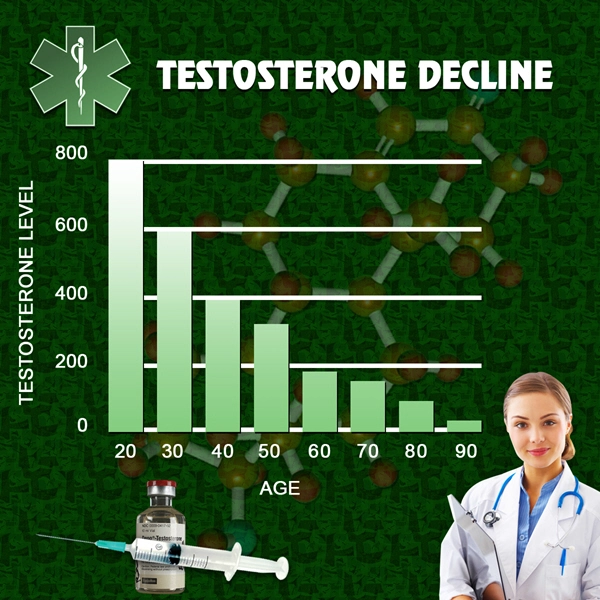
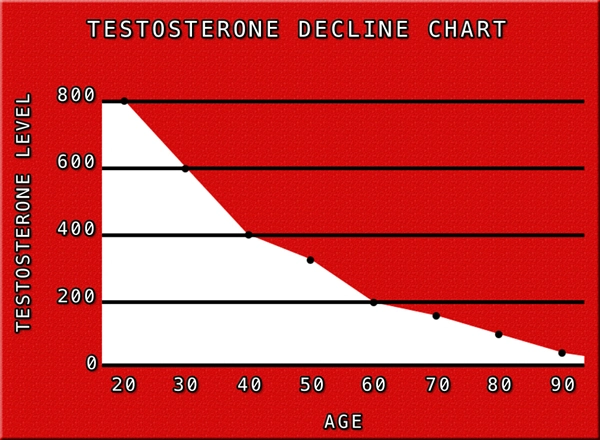
Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact male fertility, with several key hormones playing crucial roles in sperm production and overall reproductive health. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, is essential for spermatogenesis, the process by which sperm cells are produced. Low levels of testosterone, a condition known as hypogonadism, can lead to decreased sperm count and impaired fertility.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) are also vital in regulating male fertility. FSH stimulates the Sertoli cells in the testes, which support sperm development, while LH prompts the Leydig cells to produce testosterone. Imbalances in these hormones can disrupt the delicate balance required for optimal sperm production.
Common Hormonal Causes of Male Infertility
Several hormonal disorders can contribute to male infertility in the American population. One such condition is hyperprolactinemia, characterized by elevated levels of prolactin, a hormone typically associated with lactation in females. In males, high prolactin levels can inhibit the production of testosterone and gonadotropins, leading to reduced sperm production and fertility.
Another prevalent hormonal cause of male infertility is thyroid dysfunction. Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can negatively impact sperm quality and quantity. Thyroid hormones play a role in regulating metabolism and energy production, which are crucial for maintaining healthy sperm function.
Diagnosing Hormonal Imbalances in Male Infertility
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effectively addressing hormonal causes of male infertility. American males experiencing fertility issues should consult with a qualified endocrinologist or urologist specializing in male reproductive health. A comprehensive evaluation typically includes a thorough medical history, physical examination, and a series of hormonal tests, such as blood work to assess levels of testosterone, FSH, LH, prolactin, and thyroid hormones.
In some cases, additional tests like semen analysis and genetic screening may be recommended to provide a more comprehensive picture of the underlying causes of infertility.
Treatment Options for Hormonal-Related Male Infertility
The treatment of hormonal-related male infertility depends on the specific underlying cause identified through diagnostic testing. For men with hypogonadism, testosterone replacement therapy may be prescribed to restore normal hormone levels and improve sperm production. However, it's important to note that exogenous testosterone can suppress the body's natural production of sperm, so alternative approaches like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) therapy may be considered to stimulate the testes while maintaining fertility.
In cases of hyperprolactinemia, medications such as dopamine agonists can be used to lower prolactin levels and restore hormonal balance. For thyroid-related infertility, appropriate thyroid hormone replacement therapy can help normalize thyroid function and improve fertility outcomes.
Emerging Therapies and Future Directions
The field of endocrinology and male infertility is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and clinical trials exploring novel treatment options. One promising area of investigation is the use of selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) to treat hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, a condition characterized by low levels of gonadotropins and testosterone. SERMs have shown potential in stimulating the body's natural production of these hormones, offering a more targeted approach to restoring fertility.
Additionally, advancements in assisted reproductive technologies, such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), have revolutionized the treatment of male infertility. ICSI involves the direct injection of a single sperm into an egg, bypassing many of the barriers posed by hormonal imbalances and low sperm counts.
Conclusion
Hormonal imbalances play a significant role in male infertility among American males, with conditions such as hypogonadism, hyperprolactinemia, and thyroid dysfunction contributing to reduced fertility. By understanding the hormonal causes and seeking appropriate diagnosis and treatment, affected individuals can take proactive steps towards improving their reproductive health. As research continues to advance, the future holds promise for even more effective and personalized interventions, offering hope to American males navigating the challenges of infertility.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Hormonal Imbalances and Sleep Disorders: Impact on American Men's Health and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Crucial Role in Endocrine Health for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Role in Managing Chronic Fatigue in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies for Enhancing Endocrine Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Impact on Weight Management for American Males: Hormones and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hormonal Changes in Aging American Men: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Cancer Risk in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Endocrine Disorders in Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- PCOS in Transgender Men: Diagnosis, Management, and Holistic Care Approaches [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disruptors: Impact on American Male Health and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Lifestyle Impacts on Endocrine Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hormonal Optimization in Sports: Enhancing Performance Ethically for American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Male Infertility and Endocrinology: Understanding Hormonal Impacts on Fertility [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Gout in American Males: Endocrine Influences and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Impact on Sexual Health in American Males: Hormones, Dysfunction, and Holistic Care [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Kidney Health: Critical Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Mental Well-being: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Endocrine System in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Joint Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hormonal Impacts on Men's Immune Health in the U.S.: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine-Neurological Interplay in American Men: Diagnosis, Management, and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Their Role in Managing Male Depression in America [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men with Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormonal Dynamics and Skin Health in American Men: Androgens, Acne, Aging, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Prostate Cancer: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders and Heart Disease in American Men: Strategies and Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise Impacts on Endocrine Function in American Males: Hormonal Health Benefits [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders in Men: Impact on Skin Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Type 2 Diabetes in American Men: Endocrine Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine System and Liver Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine and Gastrointestinal Health Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Muscle Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health's Impact on Respiratory Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exploring ADHD and Endocrinology: Hormonal Imbalances and New Treatment Avenues [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring Endocrinological Interventions for PTSD in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Role in Managing Insomnia Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Vital Role in Treating Male Eating Disorders in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Stress Impact on Male Endocrine Health: Hormones and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Endocrine Health in American Men: Testosterone, Thyroid, and More [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Hearing Loss in American Males: Causes and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Foot Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Caffeine's Impact on Endocrine Health in American Males: Cortisol, Insulin, Testosterone, Thyroid [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Vision: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hormonal Fluctuations and Oral Health in American Men: Insights and Recommendations [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hormonal Hair Loss in American Men: Causes, Treatments, and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Male Anxiety: Endocrinological Insights and Treatments in the USA [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Sleep's Impact on Endocrine Health: Key Hormones and Practical Sleep Improvement Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Endocrine System's Impact on Digestive Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Impact on Endocrine Health in American Males: Key Nutrients and Diets [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Nail Changes in American Males: A Vital Connection [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Endocrinological Approaches Enhance Bipolar Disorder Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Eye Health: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Hand Conditions in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Ear Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hormonal Fluctuations and Nasal Health in American Men: Symptoms and Management [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hydration's Crucial Role in Endocrine Health for American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Throat Conditions in American Males: Hormonal Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Schizophrenia in Males: The Role of Endocrinology in Treatment and Management [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men with Lung Conditions: An Endocrinological Approach [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Dietary Supplements' Impact on Endocrine Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormonal Balance and Heart Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Exploring Hormonal Influences on Autism in American Males: Endocrine Insights and Therapies [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Endocrine System's Impact on Blood Health in American Males: Hormones, Disorders, and Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Mental Health's Impact on Endocrine Function in American Males: An Integrated Approach [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Exploring Endocrine Approaches to Treating OCD in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Endocrine and Nerve Health in American Males: Hormones, Disorders, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men with Kidney Disease: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hormonal Balance and Brain Health in American Men: Endocrinology Insights [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Skin Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in Men with Muscle Conditions: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Exploring Endocrine Therapy for Managing ADD Symptoms in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Crucial Role in Treating Male Eating Disorders in the USA [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Heart Health: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Choices Impact Endocrine Health in American Males: Diet, Exercise, Stress, Sleep, Substance Abuse [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Aging and Endocrine Function in American Males: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Liver Function: Impacts on American Males' Wellness [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Bone Health in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health's Impact on Joint Function in American Males: Hormonal Connections [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Impact on Male Health: Hormones, Aging, and Wellness [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Thyroid Health in American Men: Understanding Disorders, Symptoms, and Management [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 685