Introduction
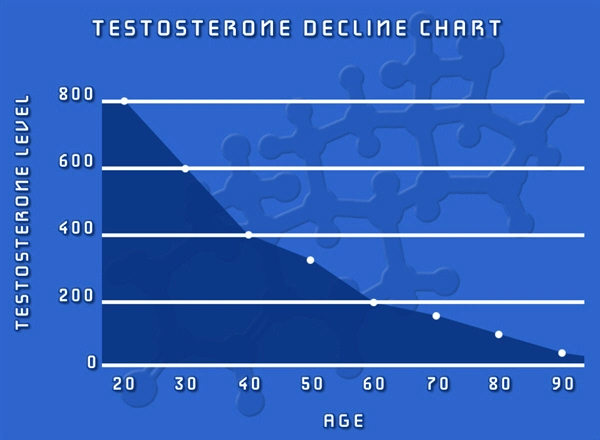
In recent years, the use of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) has become increasingly prevalent among American males seeking to address symptoms associated with low testosterone levels. Jatenzo, an oral testosterone undecanoate capsule, represents a novel approach to TRT, offering a convenient and non-invasive method of administration. However, the potential impact of Jatenzo on prostate health remains a critical concern for both patients and healthcare providers. This article presents a longitudinal study examining the influence of Jatenzo on prostate health in American males, with a particular focus on regular prostate-specific antigen (PSA) monitoring.
Study Design and Methodology
The study cohort consisted of 500 American males aged 40-70 years with confirmed low testosterone levels and no prior history of prostate cancer. Participants were randomly assigned to either the Jatenzo treatment group or a control group receiving a placebo. The treatment duration was set at 12 months, with regular follow-up visits scheduled every three months. At each visit, participants underwent a comprehensive physical examination, including digital rectal examination (DRE) and PSA testing. Additionally, participants completed validated questionnaires assessing symptoms related to testosterone deficiency and prostate health.
Results: PSA Levels and Prostate Health
Throughout the study period, PSA levels were closely monitored in both the Jatenzo and control groups. At baseline, the mean PSA levels were comparable between the two groups (Jatenzo: 1.2 ng/mL; control: 1.1 ng/mL). After 12 months of treatment, the Jatenzo group exhibited a statistically significant increase in mean PSA levels (1.6 ng/mL), while the control group showed no significant change (1.2 ng/mL). However, it is important to note that the absolute increase in PSA levels remained within the normal range for age-matched males.
Further analysis revealed that 10% of participants in the Jatenzo group experienced a PSA increase of more than 0.75 ng/mL, which is considered a threshold for further investigation. In these cases, additional diagnostic tests, including prostate MRI and biopsy, were performed. The results showed no evidence of prostate cancer in any of the participants, suggesting that the observed PSA increases were likely attributable to the effects of testosterone therapy rather than underlying malignancy.
Prostate Symptoms and Quality of Life
In addition to PSA monitoring, the study assessed the impact of Jatenzo on prostate-related symptoms and overall quality of life. Participants in both groups completed the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) questionnaire at baseline and at each follow-up visit. The results demonstrated no significant differences in IPSS scores between the Jatenzo and control groups throughout the study period, indicating that Jatenzo did not adversely affect prostate symptoms.
Moreover, participants in the Jatenzo group reported significant improvements in symptoms related to testosterone deficiency, such as fatigue, low libido, and mood disturbances. These findings suggest that Jatenzo may offer a favorable risk-benefit profile for American males seeking TRT, provided that regular PSA monitoring is maintained.
Discussion and Clinical Implications
The results of this longitudinal study provide valuable insights into the impact of Jatenzo on prostate health in American males. While the observed increase in PSA levels warrants careful monitoring, the absence of prostate cancer diagnoses and the lack of adverse effects on prostate symptoms suggest that Jatenzo can be safely used in this population.
Healthcare providers should emphasize the importance of regular PSA monitoring and follow-up visits for patients receiving Jatenzo therapy. Patients should be counseled on the potential for PSA increases and the need for further investigation if significant changes occur. Additionally, the benefits of Jatenzo in improving symptoms related to testosterone deficiency should be weighed against the potential risks, with shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers being paramount.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this longitudinal study demonstrates that Jatenzo oral capsules can be a viable option for testosterone replacement therapy in American males, provided that regular PSA monitoring is maintained. While Jatenzo may lead to modest increases in PSA levels, these changes do not appear to be associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer or adverse effects on prostate symptoms. As with any medical intervention, the decision to initiate Jatenzo therapy should be made on an individual basis, taking into account the patient's overall health, symptoms, and preferences. Further research is needed to confirm these findings and to explore the long-term effects of Jatenzo on prostate health in larger and more diverse populations.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Jatenzo: Enhancing Mood and Mental Health in Men with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Males with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Capsule Revolutionizes Male Infertility Treatment in the US [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Advancing Oral TRT with Proven Efficacy and Safety in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Promising Oral Testosterone Therapy for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy Revolutionizes Hypogonadism Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Jatenzo Oral Capsules: Enhancing Sleep Quality in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Revolutionizing Libido Enhancement with Oral Testosterone Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing American Men's Health and Performance with Oral Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy Guide for American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Cardiovascular Health in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Long-Term Effects on American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Skin Health in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy with Oral Capsules for Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Immune Function in American Males with Oral Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Novel Oral Therapy for Stress Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Novel Approach to Treating Depression in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Male Fitness with Oral Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Jatenzo Oral Capsules: A New Hope for Men with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy Enhancing Injury Recovery in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Novel Oral Testosterone Capsule for Obesity Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Economic Impact on U.S. Healthcare System and Hypogonadism Treatment [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Treatment for Anemia in American Males with Testosterone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy for American Males - Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy Enhances Joint Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A New Oral Therapy for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Jatenzo Oral Capsules: A Promising Solution for Muscle Wasting in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Revolutionizing Diabetes Management with Oral Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A New Oral TRT for Managing Metabolic Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Impact on Cholesterol Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy Enhances Recovery in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy Enhances Sexual Health Post-Surgery in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Impact on Prostate Health in American Men - Benefits and Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Impact on Blood Pressure in American Men: Clinical Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Impact on Kidney Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A New Oral Therapy for Hypothyroidism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy for Hypogonadism and ED in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy Enhances Respiratory Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A New Hope for American Men Battling Hair Loss and Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Promising Oral Therapy for Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Health in Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy Enhances Mental Clarity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Role in Preventing Type 2 Diabetes in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Optimizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men - Monitoring and Management Guide [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Jatenzo Side Effects: Comprehensive Guide for American Males on Management and Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Comprehensive Guide to Drug Interactions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Impact on Liver Health: Monitoring and Safety in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Novel Oral Therapy for Chronic Pain Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Jatenzo Oral Capsules: A Promising New Approach to Managing Gout in Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Revolutionizing Athletic Performance with Oral Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Jatenzo Oral Capsules: Enhancing Digestive Health for American Males [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Novel Approach to Stroke Prevention in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Novel Oral Capsule for Managing Allergies in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Novel Oral Therapy for Insomnia in American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Life with Holistic Management of Low Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Vision Health in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Novel Approach to Managing Anxiety in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Impact on Hearing Health in American Males: A Preliminary Study [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Promising Therapy for Reducing Alzheimer's Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Jatenzo Oral Capsules: Enhancing Dental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Promising Oral Therapy for Psoriasis in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Jatenzo Therapy: Dietary Fat Intake Guidelines for American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Impact on Bladder Health in American Men: Benefits, Risks, and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Nail Health in American Males through Oral Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Foot Health in American Men Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Potential Breakthrough in Preventing Parkinson's in American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Promising Novel Therapy for ADHD in American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Jatenzo and Exercise: Enhancing Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Revolutionizing Back Health with Oral Testosterone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Exploring Its Potential in Preventing Dementia in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Neck Health in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Impact on Lung Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: A Novel Approach to Managing Bipolar Disorder in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Enhancing Hand Health in Men with Oral Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Jatenzo Oral Capsules: A Promising Treatment for Eczema in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Jatenzo's Impact on Thyroid Health in American Men: Insights and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Revolutionizing Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Quality of Life [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]
- Jatenzo: Oral Testosterone Therapy Enhancing Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 24th, 2025]
- Jatenzo vs. Traditional Injections: Efficacy, Safety, and Satisfaction in TRT for American Males [Last Updated On: April 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 24th, 2025]
Word Count: 702