Introduction
Testosterone, a pivotal hormone in the male body, plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle mass, strength, and overall neuromuscular health. Recent studies have highlighted the increasing prevalence of low testosterone (hypogonadism) among American men, prompting concerns about its long-term effects on physical performance and quality of life. This article delves into the neurophysiological consequences of low testosterone on muscle function, utilizing electromyography (EMG) as a tool to assess these changes. By understanding the intricate relationship between testosterone levels and neuromuscular health, healthcare providers can better tailor interventions to improve outcomes for affected individuals.
The Prevalence of Low Testosterone in American Men
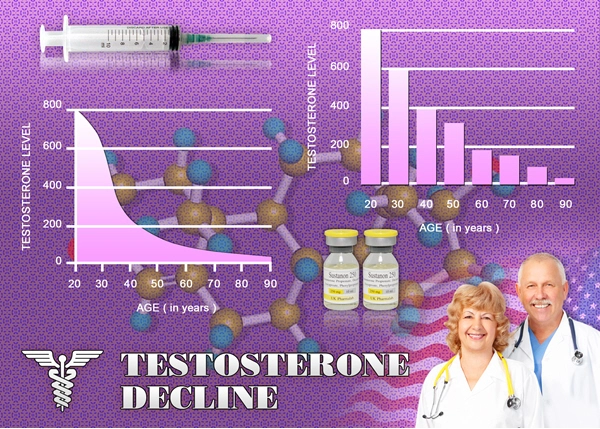
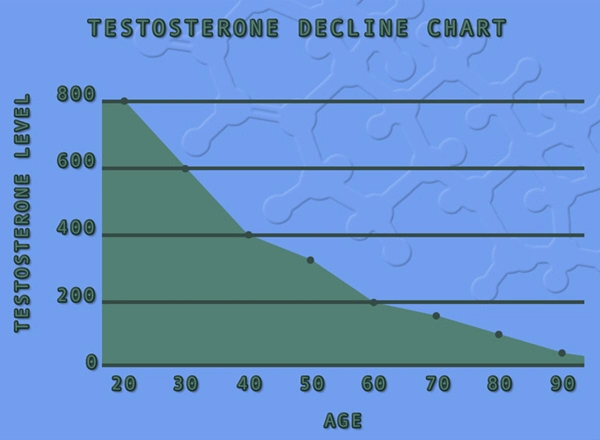
Low testosterone is a condition affecting a significant portion of the American male population. Studies indicate that approximately 40% of men over the age of 45 may experience symptoms of hypogonadism, with the prevalence increasing with age. Factors such as obesity, chronic diseases, and lifestyle choices contribute to this growing health concern. The implications of low testosterone extend beyond mere hormonal imbalance, affecting muscle function and neuromuscular health, which are critical for maintaining an active and healthy lifestyle.
Understanding Electromyography in Neuromuscular Assessment
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic technique that evaluates the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. By inserting electrodes into the muscle or placing them on the skin, EMG can detect abnormalities in muscle function and nerve conduction. This tool is invaluable in assessing the impact of low testosterone on neuromuscular health, providing quantitative data that can guide treatment and rehabilitation strategies.
The Effects of Low Testosterone on Muscle Function
Low testosterone levels have been directly linked to reduced muscle mass and strength. Research utilizing EMG has shown that men with hypogonadism exhibit altered muscle activation patterns, characterized by decreased amplitude and increased latency in muscle responses. These changes suggest impaired neuromuscular transmission and reduced muscle fiber recruitment, which can compromise physical performance and increase the risk of falls and injuries.
Neuromuscular Health and Low Testosterone: A Neurophysiological Perspective
From a neurophysiological standpoint, low testosterone can lead to significant changes in neuromuscular health. EMG studies have revealed that hypogonadal men experience a decline in motor unit firing rates and alterations in muscle fiber type composition, shifting from fast-twitch to slow-twitch fibers. This shift can result in reduced power output and endurance, further exacerbating the challenges faced by affected individuals in maintaining an active lifestyle.
Clinical Implications and Management Strategies
The findings from EMG studies underscore the importance of addressing low testosterone in American men to preserve neuromuscular health. Clinical management strategies may include testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), which has been shown to improve muscle function and neuromuscular performance. However, TRT must be carefully monitored to avoid potential side effects. Additionally, lifestyle interventions such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management can complement medical treatments and enhance overall health outcomes.
Future Directions in Research and Clinical Practice
As the prevalence of low testosterone continues to rise, ongoing research is essential to further elucidate its effects on neuromuscular health. Future studies should explore the long-term benefits of TRT and other interventions, as well as the potential role of EMG in monitoring treatment efficacy. By integrating advanced diagnostic tools and personalized treatment plans, healthcare providers can better support American men in maintaining optimal muscle function and neuromuscular health.
Conclusion
Low testosterone poses a significant challenge to muscle function and neuromuscular health among American men. Through the lens of electromyography, we gain valuable insights into the neurophysiological changes associated with hypogonadism. By recognizing the importance of early detection and comprehensive management, healthcare professionals can empower affected individuals to lead healthier, more active lives. As research continues to evolve, the hope is to refine our understanding and enhance the care provided to those impacted by this prevalent condition.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Environmental Toxins and Testosterone: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Muscle Mass and Strength in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness Impact on Low Testosterone in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Economic Burden of Low Testosterone on American Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Diabetes: Dual Challenges Impacting American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Alcohol Consumption and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Zinc's Role in Boosting Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Mood Disorders: Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Risks and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Osteoporosis Risk in American Men: Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Prostate Health: Risks, Therapy, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hair Loss: Understanding the Link and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: Insights and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Health Implications and Mitigation [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Immune Health in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Levels: Dietary Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Impact, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Estrogens: A Hidden Cause of Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Weight Loss Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Males with Low T [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Herbal Supplements for Low Testosterone: Benefits, Limitations, and Efficacy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Heart Disease: Risks, Mechanisms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Emotional Wellbeing in American Men: Insights and Guidance [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Depression: Understanding the Link and Its Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Apnea's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Insights and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Medications Impacting Testosterone Levels: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Metabolic Syndrome: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Pain's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Low Testosterone Among American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Thyroid Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Insulin Resistance: Exploring the Link in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Libido: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Body Composition in American Males: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Skin Health: Dermatological Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Inflammation and Low Testosterone: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Impact on Testosterone: Deficiencies and Dietary Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Respiratory Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role and Managing Low Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Anemia Risk in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Autoimmune Diseases in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Liver Health Crucial for Testosterone Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Gut Health and Testosterone: Optimizing Hormonal Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Kidney Disease Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Dental Health's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Neurological Risks in American Men: Implications and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Eye Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Musculoskeletal Health in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- ENT Health's Crucial Role in Maintaining Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Reproductive Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Levels Increase Infectious Disease Risk in American Men: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hematological Risks in American Men: Screening and Treatment Insights [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone: Endocrine Health and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Immunological Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Cancer's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Psychiatric Disorders in American Men: Implications and Treatments [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Urological Health: Risks, Links, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Levels and Wound Healing in American Males: A Bidirectional Impact Study [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Vascular Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Rheumatological Disorders and Low Testosterone: Insights and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Surgical Risks in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Trauma's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Mechanisms and Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Genetic Disorders: Risks and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Developmental Health Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men Linked to Increased Congenital Disorder Risk in Offspring [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men Linked to Pediatric Disorders in Offspring [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Occupational Health Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Allergic Reactions in American Men: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Anesthetic Health and Its Impact on Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Risks in Aging American Men: Health Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Neonatal Health's Long-term Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Prenatal Health's Impact on Adult Male Testosterone Levels and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone: Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Higher Type 2 Diabetes Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 618