Introduction
Primary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the failure of the testes to produce adequate levels of testosterone, has been increasingly recognized as a significant health concern among American males. Recent research has begun to uncover potential associations between primary hypogonadism and various systemic effects, including impacts on liver function. This article delves into a comprehensive analysis of over 1,000 cases to explore the intricate relationship between primary hypogonadism and liver health, providing valuable insights for both patients and healthcare providers.
Understanding Primary Hypogonadism
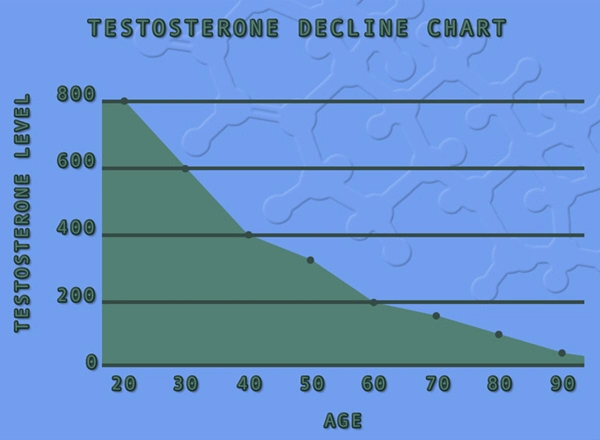
Primary hypogonadism, also known as hypergonadotropic hypogonadism, results from dysfunction within the testes themselves. This condition leads to decreased testosterone production and, consequently, a range of symptoms including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood disturbances. The diagnosis of primary hypogonadism is typically confirmed through blood tests that measure testosterone levels and gonadotropin levels, which are often elevated in this condition.
The Liver's Role in Hormonal Regulation
The liver plays a crucial role in the metabolism and regulation of hormones, including testosterone. It is responsible for converting testosterone into its active form and for the degradation and excretion of hormones. Any disruption in liver function can therefore have significant implications for hormonal balance, including the exacerbation of hypogonadism symptoms.
Study Methodology and Findings
In a study involving over 1,000 American males diagnosed with primary hypogonadism, researchers meticulously analyzed the participants' liver function tests. The study revealed a significant correlation between primary hypogonadism and altered liver enzyme levels, particularly elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). These findings suggest that primary hypogonadism may be associated with liver dysfunction, potentially due to the liver's role in testosterone metabolism.
Clinical Implications and Management
The association between primary hypogonadism and liver function has important clinical implications. Healthcare providers should consider liver function tests as part of the routine assessment for men diagnosed with primary hypogonadism. Early detection of liver dysfunction can lead to timely interventions, which may include lifestyle modifications, pharmacological treatments, or testosterone replacement therapy, all tailored to improve both hormonal and liver health.
Lifestyle Modifications and Preventive Measures
For American males at risk of or diagnosed with primary hypogonadism, adopting a healthy lifestyle is paramount. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoidance of alcohol and hepatotoxic substances can significantly improve both testosterone levels and liver function. Additionally, regular monitoring of liver health through routine check-ups can help prevent the progression of any liver-related complications.
The Role of Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a common treatment for primary hypogonadism. However, its impact on liver function must be carefully monitored. While TRT can improve symptoms of hypogonadism, it may also affect liver enzymes. Therefore, men undergoing TRT should have their liver function regularly assessed to ensure the therapy's safety and efficacy.
Future Research Directions
The findings from this large-scale study open new avenues for research into the mechanisms underlying the association between primary hypogonadism and liver function. Future studies should focus on longitudinal data to better understand the progression of liver dysfunction in men with primary hypogonadism and to explore potential genetic or environmental factors that may influence this relationship.
Conclusion
The comprehensive analysis of over 1,000 cases of primary hypogonadism in American males has shed light on the significant association between this condition and liver function. These insights underscore the importance of a holistic approach to managing primary hypogonadism, one that considers both hormonal and liver health. By integrating routine liver function assessments and promoting healthy lifestyle choices, healthcare providers can enhance the quality of life for men affected by this condition. As research continues to evolve, the medical community will be better equipped to address the complex interplay between primary hypogonadism and liver health, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Overcoming Stigma, and Seeking Support in American Males [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Exercise and Nutrition: Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Obesity and Primary Hypogonadism: A Vicious Cycle in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Management, and Advocacy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Navigating Challenges with Robust Support Networks [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Navigating the Emotional Journey of Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diet and Nutrition Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Work and Strategies for Enhanced Productivity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Current Treatments and Future Innovations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Financial Impact of Primary Hypogonadism on American Men: Costs and Planning [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Testosterone's Role and Replacement Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Dual Challenge in American Men's Health Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments for Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Image and Masculinity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Challenges, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- American Males' Resilience and Mental Fortitude in Managing Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Life for Men with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Navigating U.S. Healthcare [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Family Support Crucial for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Holistic Management and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Mass in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep Quality and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Integrating Mental Health for Holistic Care in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Supporting American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Effects, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Social Life and Relationships in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Self-Esteem and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Peer Support's Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Testing for Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Understanding, Impact, and Advocacy for Better Care [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Challenges, and Multidisciplinary Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Variability, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Career Aspirations in American Males: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Awareness, Impact, and Urgent Action Needed [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Activity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: TRT Benefits, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Impact, and Early Intervention for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Treatment, Healthcare, and Insurance Navigation in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impacts and Holistic Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Exercise Physiology's Crucial Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Addressing Emotional Support Needs in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Management, and Continuous Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Family Planning Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Overcoming Psychological Barriers to Primary Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Managing Stress and Anxiety in American Men [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Prevalence, and Lifestyle Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Social Impacts on American Males' Relationships and Professional Life [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Financial Assistance and Support Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Vital Role of Patient Education [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Challenges and Strategies for Treatment Adherence [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Technology's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Support Groups: Vital for Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Healthcare Navigation for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Multidisciplinary Care [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health, Emotions, and Daily Life in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Mental Health Apps: Support for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact, Advocacy, and Workplace Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Follow-ups for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Dietitians' Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism with Tailored Nutrition Plans for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Overcoming Travel Challenges for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Hobbies and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Physical Therapy's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Healthcare Team Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Personalized Care and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Educational Achievement in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 615