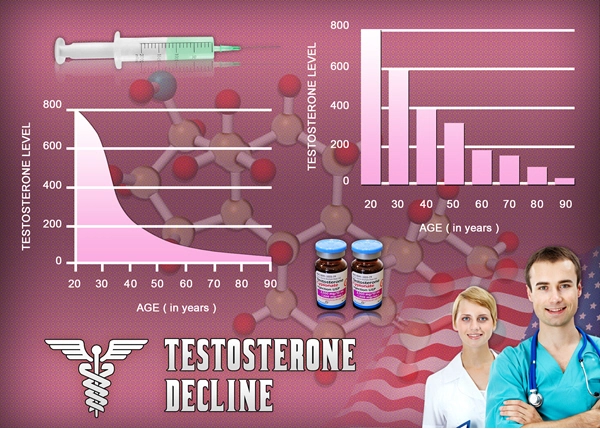
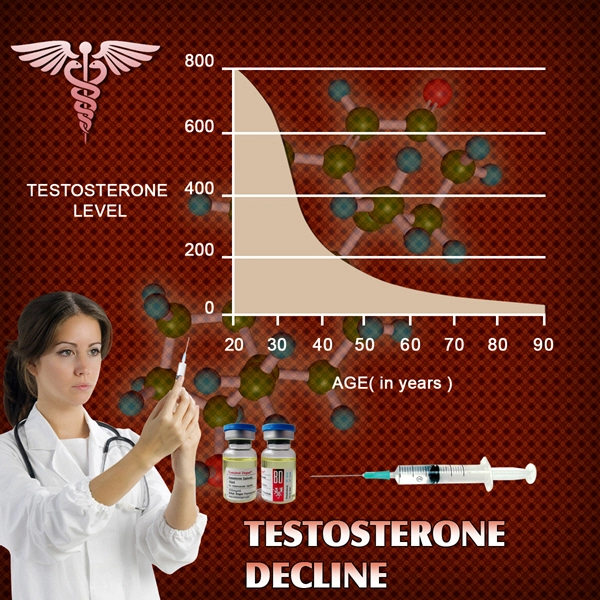
Introduction
Primary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone by the testes, has profound implications on the physical health of affected individuals. However, the psychological ramifications of this condition are equally significant, yet often underexplored. This article delves into a qualitative study that involved in-depth interviews with over 100 American males diagnosed with primary hypogonadism, aiming to shed light on the emotional and psychological challenges they face. Understanding these impacts is crucial for healthcare providers to offer comprehensive care that addresses both the physical and mental well-being of their patients.
The Emotional Landscape of Primary Hypogonadism
The study revealed a complex emotional landscape among men with primary hypogonadism. Participants frequently reported feelings of frustration and helplessness due to the physical symptoms of their condition, such as reduced libido, fatigue, and muscle weakness. These physical manifestations often led to a diminished sense of masculinity and self-worth, with many men expressing concerns about their ability to fulfill traditional male roles within their families and society.
Impact on Mental Health
A significant finding from the interviews was the high prevalence of mental health issues among the participants. Depression and anxiety were common, with many men struggling to cope with the chronic nature of their condition. The emotional burden was compounded by societal pressures to maintain a facade of strength and resilience, making it challenging for these men to seek help or openly discuss their struggles. The study highlighted the need for mental health support tailored to the unique needs of men with primary hypogonadism.
Social and Relationship Dynamics
The psychological impact of primary hypogonadism extended beyond individual mental health, affecting social interactions and relationships. Participants reported difficulties in their intimate relationships, often stemming from reduced sexual desire and performance anxiety. The strain on romantic partnerships was a recurring theme, with some men experiencing feelings of guilt and inadequacy. Additionally, the condition affected friendships and professional relationships, as participants felt less capable of engaging in social activities or maintaining their previous levels of productivity at work.
Coping Mechanisms and Resilience
Despite the challenges, the study also uncovered various coping mechanisms employed by men with primary hypogonadism. Some participants found solace in support groups, where they could share experiences and strategies for managing their condition. Others turned to physical activities that were still within their capabilities, emphasizing the importance of maintaining an active lifestyle to bolster mental health. The resilience displayed by these men underscores the potential for positive adaptation and the critical role of community and healthcare support in fostering this resilience.
Healthcare Implications and Recommendations
The findings of this qualitative study have important implications for healthcare providers. It is essential for clinicians to recognize the psychological dimensions of primary hypogonadism and to integrate mental health screening and support into the management of the condition. Education about the psychological effects of hypogonadism should be provided to patients and their families to foster understanding and empathy. Furthermore, healthcare systems should facilitate access to mental health resources, including counseling and support groups, to help men navigate the emotional challenges of living with primary hypogonadism.
Conclusion
The psychological impact of primary hypogonadism on American males is profound and multifaceted, affecting their mental health, relationships, and overall quality of life. This qualitative study provides valuable insights into the lived experiences of men with this condition, highlighting the need for a holistic approach to care that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of primary hypogonadism. By acknowledging and addressing these psychological challenges, healthcare providers can significantly improve the well-being of their patients, helping them to lead fulfilling and resilient lives despite the hurdles posed by their condition.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Overcoming Stigma, and Seeking Support in American Males [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Exercise and Nutrition: Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Obesity and Primary Hypogonadism: A Vicious Cycle in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Management, and Advocacy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Navigating Challenges with Robust Support Networks [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Navigating the Emotional Journey of Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diet and Nutrition Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Work and Strategies for Enhanced Productivity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Current Treatments and Future Innovations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Financial Impact of Primary Hypogonadism on American Men: Costs and Planning [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Testosterone's Role and Replacement Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Dual Challenge in American Men's Health Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments for Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Image and Masculinity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Challenges, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- American Males' Resilience and Mental Fortitude in Managing Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Life for Men with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Navigating U.S. Healthcare [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Family Support Crucial for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Holistic Management and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Mass in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep Quality and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Integrating Mental Health for Holistic Care in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Supporting American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Effects, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Social Life and Relationships in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Self-Esteem and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Peer Support's Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Testing for Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Understanding, Impact, and Advocacy for Better Care [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Challenges, and Multidisciplinary Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Variability, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Career Aspirations in American Males: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Awareness, Impact, and Urgent Action Needed [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Activity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: TRT Benefits, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Impact, and Early Intervention for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Treatment, Healthcare, and Insurance Navigation in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impacts and Holistic Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Exercise Physiology's Crucial Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Addressing Emotional Support Needs in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Management, and Continuous Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Family Planning Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Overcoming Psychological Barriers to Primary Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Managing Stress and Anxiety in American Men [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Prevalence, and Lifestyle Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Social Impacts on American Males' Relationships and Professional Life [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Financial Assistance and Support Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Vital Role of Patient Education [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Challenges and Strategies for Treatment Adherence [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Technology's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Support Groups: Vital for Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Healthcare Navigation for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Multidisciplinary Care [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health, Emotions, and Daily Life in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Mental Health Apps: Support for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact, Advocacy, and Workplace Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Follow-ups for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Dietitians' Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism with Tailored Nutrition Plans for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Overcoming Travel Challenges for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Hobbies and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Physical Therapy's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Healthcare Team Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Personalized Care and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Educational Achievement in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 601