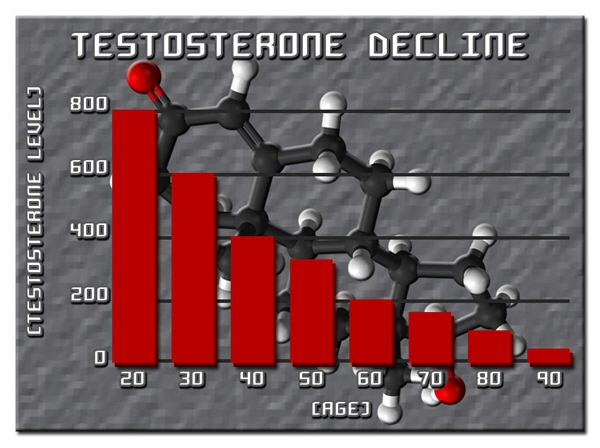
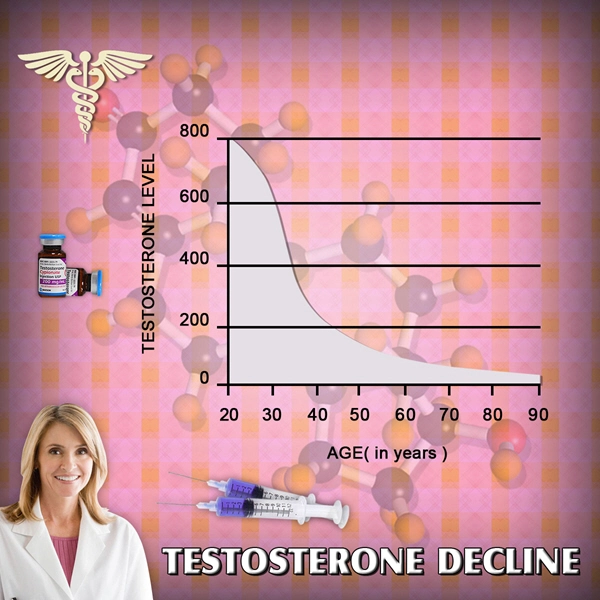
Introduction
Testim Testosterone Gel, a commonly prescribed treatment for hypogonadism in American males, has been the subject of increasing interest due to its potential impact on various bodily systems. While its effects on libido, muscle mass, and mood are well-documented, the influence of testosterone supplementation on digestive health remains less explored. This article presents findings from a year-long study focused on the gastrointestinal effects of Testim Testosterone Gel in American males, offering insights into its safety and efficacy from a digestive health perspective.
Study Design and Methodology
The study involved 200 American males aged between 30 and 65 years, all diagnosed with hypogonadism and prescribed Testim Testosterone Gel. Participants were monitored over a period of one year, with regular assessments of their digestive health. Key parameters included gastrointestinal symptoms, liver function tests, and changes in gut microbiota. The study employed a combination of self-reported questionnaires, clinical examinations, and laboratory analyses to gather comprehensive data.
Impact on Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Throughout the study, participants reported various gastrointestinal symptoms, which were tracked and analyzed. Initially, a small percentage of participants experienced mild digestive discomfort, such as bloating and indigestion, within the first three months of treatment. However, these symptoms were transient and resolved without intervention. By the end of the year, no significant increase in gastrointestinal complaints was observed compared to baseline levels. This suggests that Testim Testosterone Gel does not adversely affect digestive health in the long term.
Liver Function and Testosterone Gel
Liver health is a critical concern when considering hormone supplementation. The study monitored liver function through regular blood tests, focusing on enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). The results indicated no significant changes in liver enzyme levels over the year, suggesting that Testim Testosterone Gel does not impair liver function. This finding is reassuring for clinicians and patients considering testosterone therapy.
Gut Microbiota and Hormonal Balance
The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in overall health, including digestion and immune function. The study included analysis of stool samples to assess changes in gut microbiota composition. While testosterone therapy did not lead to significant alterations in the overall diversity of gut bacteria, there were subtle shifts in certain microbial species. These changes were not associated with adverse health outcomes and may reflect the body's adaptation to hormonal supplementation.
Patient Experiences and Quality of Life
Participants' subjective experiences and quality of life were also assessed. Many reported improvements in energy levels, mood, and overall well-being, which are typical benefits of testosterone therapy. Importantly, these positive changes were not overshadowed by gastrointestinal issues, reinforcing the safety profile of Testim Testosterone Gel. Participants' feedback highlighted the importance of regular monitoring and communication with healthcare providers to manage any potential side effects effectively.
Conclusion
This year-long study provides valuable insights into the impact of Testim Testosterone Gel on digestive health in American males. The findings indicate that the gel does not lead to significant gastrointestinal problems or liver dysfunction, and any initial digestive symptoms tend to be temporary. While subtle shifts in gut microbiota were observed, these were not linked to adverse health effects. Overall, Testim Testosterone Gel appears to be a safe and effective treatment for hypogonadism, with minimal impact on digestive health.
Future Directions
Further research is warranted to explore the long-term effects of testosterone supplementation on digestive health and to investigate the potential benefits of personalized treatment approaches. As the understanding of the gut microbiome continues to evolve, future studies may provide additional insights into the complex interplay between hormones and gastrointestinal function.
In conclusion, this study underscores the importance of comprehensive monitoring and patient education when prescribing Testim Testosterone Gel. By understanding its effects on digestive health, healthcare providers can better support American males in managing hypogonadism and optimizing their overall well-being.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Vitality in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testim Gel: Enhancing Life Quality in Age-Related Testosterone Decline for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits and Usage for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits, Risks, and Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testim: Tailored Testosterone Therapy for American Men's Health and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits, Side Effects, and Usage Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Men's Health in the US [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Male Health and Well-being in America [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testim Gel: Enhancing Life Quality for American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testim Gel: Importance of Monitoring Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Optimal TRT Choice for American Males' Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Effective Low Testosterone Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Safety, Benefits, and Risks for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Vitality and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Absorption, Effectiveness, and Safety in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits, Application, and Safety for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Bone Density and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Vitality in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Health and Vitality in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Men's Health and Well-being in America [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Combating Fatigue in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Men's Health and Vitality in the US [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel Enhances Cognitive Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Usage, Benefits, and Safety for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Muscle Growth and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Psychological Well-being in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Revolutionizing Male Health in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Convenient Solution for American Men's Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits, Side Effects, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Fertility in American Men - Mechanism and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testim Gel: Enhancing Vitality in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testim Gel: Boosting Libido and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Mood in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testim Gel: Effective Hypogonadism Treatment with Safety Considerations [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing American Men's Health and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Athletic Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Sleep Quality in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits and Management for Diabetic American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Skin Health Impacts and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Safety, Risks, and Benefits for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Solution for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Managing Low Testosterone in Obese American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Preventing Muscle Loss in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Promising Tool for Stress Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits and Risks for American Men with Heart Disease [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Effects on Hair Growth in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel's Impact on Prostate Health in American Males: Current Insights [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Testim Gel: A Promising Treatment for Chronic Fatigue in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Post-Surgical Recovery in American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testim Gel: Managing Hypogonadism and Hypertension in American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Impacts on Joint Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testim Gel: Enhancing Life for American Men with Autoimmune Disorders [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits for American Men with Thyroid Issues [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Sleep Quality in American Men with Sleep Apnea [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Liver Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Impacts on Digestive Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Effects on Kidney Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Promising Treatment for Chronic Pain in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testim Gel: Effective Testosterone Replacement for American Men with Allergies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Promising Treatment for Anxiety in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Vision in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Effective HRT for American Men with Skin Conditions [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits and Considerations for Arthritis in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Benefits and Risks for Neurological Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Respiratory Health in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Dental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel's Impact on Hearing in American Men: Current Findings and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Solution for Men with Gastrointestinal Issues and Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Impacts on Nail Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: Enhancing Health and Well-being in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Testim Testosterone Gel: A Promising Anti-Inflammatory Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 623