Introduction
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) has become increasingly prevalent among American men seeking to mitigate the symptoms of hypogonadism and age-related testosterone decline. While the benefits of TRT on sexual function, muscle mass, and mood are well-documented, emerging research suggests a potential link between TRT and gastrointestinal health, specifically gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This article delves into the association between TRT and GERD, providing American men with crucial insights into managing their health effectively.
Understanding Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
GERD is a chronic condition characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. It affects a significant portion of the American population, with men being particularly susceptible due to lifestyle factors and physiological differences. The prevalence of GERD necessitates a thorough understanding of its potential triggers, including the role of hormonal therapies like TRT.
The Link Between Testosterone and GERD
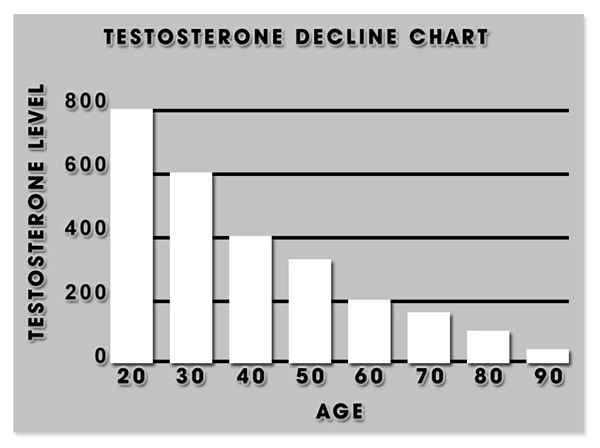
Recent studies have begun to explore the relationship between testosterone levels and GERD. Testosterone, a hormone integral to male physiology, influences various bodily functions, including muscle tone and fat distribution. Research indicates that fluctuations in testosterone levels may affect the lower esophageal sphincter's (LES) ability to prevent acid reflux. Specifically, lower testosterone levels have been associated with decreased LES pressure, which could exacerbate GERD symptoms.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Its Effects
TRT aims to restore testosterone levels to normal ranges, potentially alleviating symptoms of hypogonadism. However, the impact of TRT on GERD remains a subject of ongoing research. Some studies suggest that TRT may improve LES function by increasing muscle tone, thereby reducing the incidence of acid reflux. Conversely, other research indicates that TRT could lead to increased abdominal fat, a known risk factor for GERD.
Clinical Evidence and Considerations
A recent gastrointestinal study conducted in the United States examined the association between TRT and GERD in a cohort of American men. The study found that men on TRT reported a higher incidence of GERD symptoms compared to those not receiving the therapy. This finding underscores the need for healthcare providers to monitor GERD symptoms in patients undergoing TRT and consider alternative management strategies.
Managing GERD in Men on TRT
For American men considering or currently undergoing TRT, managing GERD effectively is paramount. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding trigger foods, and elevating the head during sleep, can significantly alleviate symptoms. Additionally, healthcare providers may recommend proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers to manage acid production and reduce reflux.
Future Research Directions
The relationship between TRT and GERD warrants further investigation to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and optimize treatment strategies. Future studies should focus on longitudinal data to assess the long-term impact of TRT on GERD and explore the potential benefits of tailored hormonal therapies that address both hypogonadism and gastrointestinal health.
Conclusion
The association between testosterone replacement therapy and gastroesophageal reflux disease in American men is a complex and evolving field of study. While TRT offers numerous benefits, its potential impact on GERD necessitates careful consideration and monitoring. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers, American men can navigate the challenges of TRT and GERD, ensuring a balanced approach to their overall health and well-being.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- TRT's Impact on Mental Health in American Men: Depression, Anxiety, and Cognition [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Economic Impact of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on U.S. Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- TRT: Understanding Impacts on Prostate Health and Cancer Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: American Men's Experiences and Impact on Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Optimizing TRT: Diet, Exercise, and Holistic Health for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance for Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Dosage, Administration, and Lifestyle Integration for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Enhancing TRT Outcomes with Alternative Therapies: A Holistic Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Future of TRT: Innovations and Impacts on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits and Risks for Young American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT Improves Sleep Quality in American Males with Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT: Managing Hypogonadism in American Males - Benefits, Risks, and Future Trends [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Combating Fatigue in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT Boosts Bone Health in American Males: Benefits, Evidence, and Lifestyle Integration [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Cultural Attitudes and Masculinity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Managing Side Effects in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Muscle Mass in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Immune Function: Benefits, Risks, and Monitoring in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Process for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Monitoring, Adjustments, and Lifestyle Integration for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT in American Men: Balancing Benefits with Hair Loss Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Mood and Vitality in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT: Benefits and Risks for Vision Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Potential in Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Joint Health in American Males Through Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Weight Management in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT Impact on Male Fertility: Risks, Alternatives, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Realistic Expectations for Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Cost-Benefit Analysis and Accessibility in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Stamina and Vitality in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT's Role in Enhancing Injury Recovery Among American Males: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT: A Promising Approach to Managing Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT: A Promising Approach to Stress Management in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Kidney Health: Benefits, Risks, and Monitoring for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Holistic Approaches for Low Libido [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT and Liver Health: Risks, Monitoring, and Mitigation Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Diabetes: Benefits, Risks, and Personalized Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT Benefits for American Males: Enhancing Skin Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT Boosts Confidence and Vitality in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Side Effects for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Men: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Digestive Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Effects with Lifestyle Changes for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Choosing the Right TRT Clinic: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Blood Pressure: Risks, Benefits, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Cholesterol: Essential Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Restoring Vitality in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Thyroid Function: Monitoring and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Blood Sugar: Insights for American Men Considering Therapy [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Navigating Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Understanding and Interpreting Lab Results [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Athletic Performance Safely and Ethically [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Allergic Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Dental Health: Insights and Recommendations for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Maximizing TRT Benefits: Integrating Therapy with Lifestyle and Supplements for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- TRT and Hearing Health: Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Guide to Managing Testosterone Replacement Therapy While Traveling [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Social Life and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Eye Health: Benefits for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Male Fertility: Risks, Evidence, and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Nail Health: Benefits, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Hand Health in American Men: Strength, Dexterity, and Joints [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Exploring Social Implications of Testosterone Replacement Therapy in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Work Performance in American Males - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Artistic Expression in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Neck Health: Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Foot Health in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Ethical Considerations in Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- TRT Impact on Chest Health: Benefits, Risks, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Psychological Benefits and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Back Health in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Glycemic Control in American Men with Type 2 Diabetes: Cohort Study [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Male Health and Addressing Low Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
Word Count: 532