Introduction
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that significantly impacts the quality of life of affected individuals. Characterized by symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia, PD predominantly affects older adults, with a notable prevalence among American males. Recent studies have begun to explore the potential therapeutic benefits of testosterone enanthate, a long-acting form of testosterone, in managing PD symptoms. This article delves into the effects of testosterone enanthate on Parkinson's disease symptoms in American males, offering insights into its neurological implications.
Understanding Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease results from the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain crucial for motor control. The loss of these neurons leads to a dopamine deficiency, which manifests as the hallmark symptoms of PD. While the exact cause of PD remains elusive, both genetic and environmental factors are believed to play roles in its development. In the United States, PD affects approximately 500,000 individuals, with men being 1.5 times more likely to develop the disease than women.
The Role of Testosterone in Neurological Health
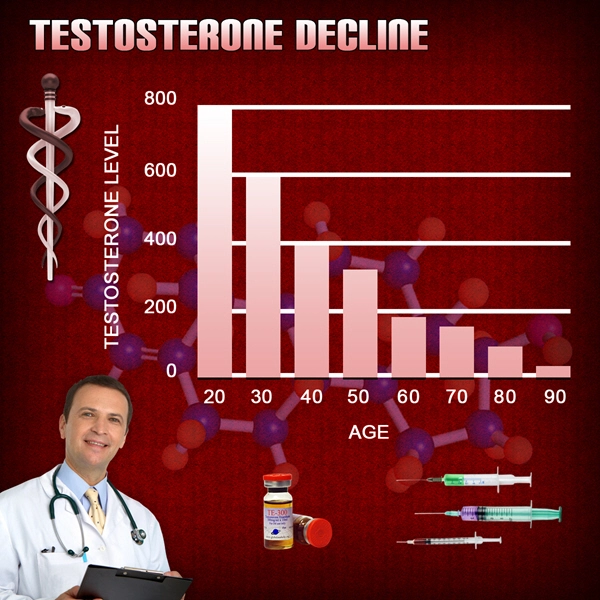
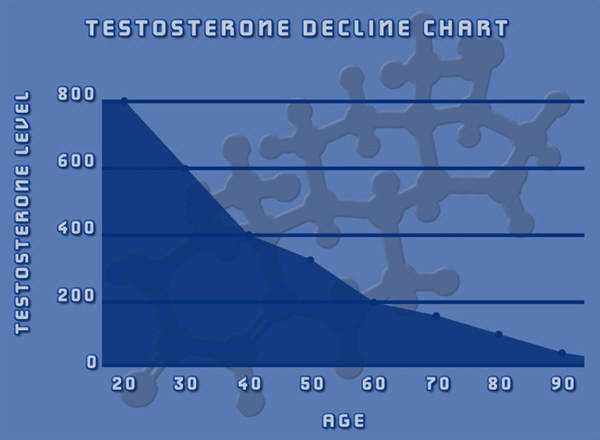
Testosterone, primarily known for its role in male sexual development, also has significant neurological functions. It influences neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and neurogenesis, which are critical for maintaining cognitive and motor functions. As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, which may exacerbate the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like PD. This has led researchers to investigate whether testosterone supplementation could offer therapeutic benefits for PD patients.
Testosterone Enanthate and Parkinson's Disease: The Study
A recent study conducted in the United States focused on the effects of testosterone enanthate on PD symptoms in American males. The study included a cohort of men aged 50 to 75 with confirmed PD diagnoses. Participants were administered weekly injections of testosterone enanthate over a 12-month period, while a control group received placebo injections. The primary outcomes measured were changes in motor function, cognitive performance, and quality of life.
Findings on Motor Function
The study found that participants receiving testosterone enanthate exhibited significant improvements in motor function compared to the placebo group. Specifically, there were reductions in tremor severity and rigidity, as well as enhancements in gait and balance. These improvements were assessed using standardized scales such as the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), which showed statistically significant differences between the two groups.
Cognitive and Quality of Life Outcomes
In addition to motor function, the study evaluated cognitive performance and quality of life. Participants in the testosterone enanthate group demonstrated better performance on cognitive tests, particularly those measuring executive function and memory. Moreover, self-reported quality of life scores were higher in the treatment group, suggesting that testosterone supplementation may have a positive impact on the overall well-being of PD patients.
Mechanisms of Action
The beneficial effects of testosterone enanthate on PD symptoms are thought to be mediated through several mechanisms. Testosterone may enhance dopaminergic transmission by increasing the expression of dopamine receptors and transporters. Additionally, it may promote neuroprotection by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which are implicated in the progression of PD. These mechanisms highlight the potential of testosterone enanthate as a multifaceted therapeutic agent for PD.
Considerations and Future Directions
While the study's findings are promising, several considerations must be addressed. The long-term safety and efficacy of testosterone enanthate in PD patients require further investigation. Potential side effects, such as cardiovascular risks and prostate issues, need to be carefully monitored. Future research should also explore the optimal dosing and duration of treatment to maximize benefits while minimizing adverse effects.
Conclusion
The study on the effects of testosterone enanthate on Parkinson's disease symptoms in American males offers a hopeful outlook for managing this debilitating condition. By improving motor function, cognitive performance, and quality of life, testosterone enanthate presents a potential therapeutic avenue for PD patients. As research continues, it is crucial to balance the benefits and risks to ensure the best possible outcomes for those affected by Parkinson's disease.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Associated Risks in the US [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Long-Term Health Risks of Testosterone Enanthate Use in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Low Testosterone Treatment [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Sleep Quality in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Dispelling Myths and Understanding Facts for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Cognitive Function in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Prostate Risks, and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Cycle: Enhancing Performance and Managing Risks in Athletes [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Personalization, Monitoring, and Lifestyle Integration for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Blood Sugar Levels in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Withdrawal: Symptoms and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Male Fertility: Insights for American Patients [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Obesity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Ethical Dilemmas of Testosterone Enanthate Use Among American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Enhancing Veteran Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Effects on Hair Growth and Loss in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Appetite and Digestion in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential New Treatment for Allergies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Injury Recovery in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Joint Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Anemia in Hypogonadal American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Endurance in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Cultural Perceptions and Masculinity in American Society [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Combating Age-Related Decline in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Solution for Muscle Wasting in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Process, and Risks for Men Over 50 [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Stress Management Tool for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Skin Elasticity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Treatment for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Endurance in American Male Athletes - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Limitations, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat, Boosting Performance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: Risks and Recommendations [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Vision and Eye Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Costs, and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Dosage, Monitoring, and Lifestyle for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Impacts on Life Expectancy and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Post-Surgical Recovery in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Respiratory Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Autoimmune Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Role in Managing Diabetes in American Men: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Kidney Function Impact in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Hearing Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Liver Health in American Men: Risks and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Hypertension in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Male Reproductive Health and Fertility in America [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Treatment for Gastrointestinal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Neurological Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Adrenal Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle and Bone Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Thyroid Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Endocrine Impact in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Respiratory Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Males: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Emerging Role in Dermatology for American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Hematological Health in American Men: Benefits and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Metabolic Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Neurological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Metabolic Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: An Analysis [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Potential Benefits for Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Impacts and Management of Reproductive Health in Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Key Role in Treating Hypogonadism and Enhancing Male Health [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Potential Treatment for Hematological Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Gastrointestinal Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Neurological Impact on American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Effective Management of Low T in American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 647