Introduction
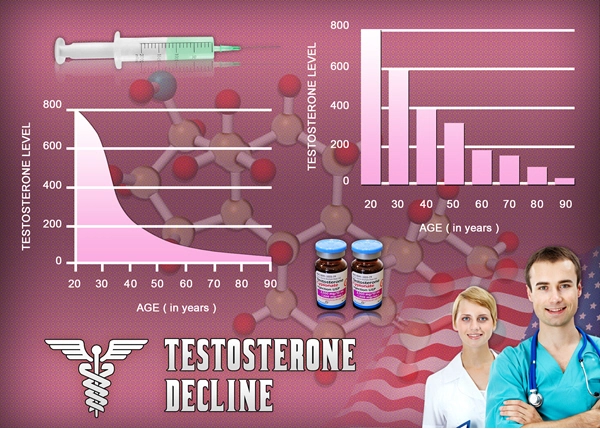
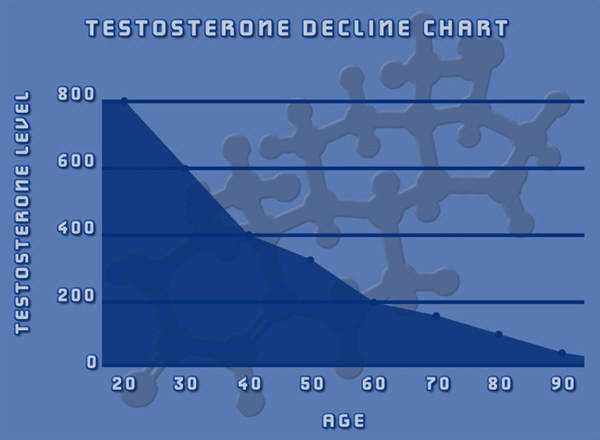
Peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves, manifests in symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and pain, primarily affecting the extremities. The prevalence of this condition among American males has prompted extensive research into potential therapeutic interventions. One such intervention that has garnered attention is the use of testosterone enanthate, a synthetic form of testosterone. This article delves into the neurological impact of testosterone enanthate on peripheral neuropathy in American males, exploring its potential benefits and limitations.
Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy can arise from various causes, including diabetes, infections, and exposure to toxins. In the United States, diabetic neuropathy is particularly prevalent among males, contributing significantly to the overall burden of the disease. The condition not only affects the quality of life but also poses challenges in management and treatment. Traditional therapies often focus on symptom management rather than addressing the underlying pathology, thus highlighting the need for novel therapeutic approaches.
The Role of Testosterone Enanthate
Testosterone enanthate is an esterified form of testosterone used primarily for hormone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men. Its long-acting nature allows for less frequent administration, making it a convenient option for patients. Beyond its role in hormone replacement, recent studies have suggested that testosterone enanthate may have neuroprotective effects, potentially beneficial in the context of peripheral neuropathy.
Neurological Impact on Peripheral Neuropathy
Emerging research indicates that testosterone enanthate may influence nerve regeneration and repair. Studies have shown that testosterone can enhance the expression of neurotrophic factors, which are essential for the survival and function of neurons. In animal models, testosterone administration has been associated with improved nerve conduction velocities and reduced neuropathic pain, suggesting a potential therapeutic role in human patients.
Clinical Evidence in American Males
Clinical trials involving American males with peripheral neuropathy have provided preliminary insights into the effects of testosterone enanthate. A notable study conducted at a leading American university involved a cohort of diabetic men with established neuropathy. Participants receiving testosterone enanthate reported significant improvements in neuropathic symptoms compared to the placebo group. Pain scores decreased, and sensory function improved, indicating a positive impact on the peripheral nervous system.
Mechanisms of Action
The mechanisms through which testosterone enanthate exerts its effects on peripheral neuropathy are multifaceted. Testosterone is known to modulate inflammation, a key contributor to nerve damage. By reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines, testosterone may mitigate the inflammatory response associated with neuropathy. Additionally, testosterone's role in enhancing vascular health could improve blood flow to affected nerves, facilitating repair and regeneration.
Considerations and Limitations
While the potential benefits of testosterone enanthate in treating peripheral neuropathy are promising, several considerations must be addressed. The use of testosterone therapy is not without risks, including cardiovascular complications and the potential for exacerbating prostate conditions. Therefore, careful patient selection and monitoring are essential. Furthermore, the long-term effects of testosterone enanthate on peripheral neuropathy remain unclear, necessitating further research to establish its safety and efficacy over extended periods.
Future Directions
The exploration of testosterone enanthate as a therapeutic option for peripheral neuropathy in American males is an evolving field. Future studies should focus on larger, more diverse patient populations to validate initial findings. Additionally, research into the optimal dosing and duration of therapy will be crucial in maximizing benefits while minimizing risks. Collaborative efforts between neurologists, endocrinologists, and researchers will be instrumental in advancing our understanding and application of testosterone enanthate in the management of peripheral neuropathy.
Conclusion
Testosterone enanthate presents a promising avenue for the treatment of peripheral neuropathy in American males. Its potential neuroprotective and regenerative effects offer hope for improved outcomes in patients suffering from this debilitating condition. However, the journey from promising research to clinical practice requires rigorous scientific validation and careful consideration of associated risks. As the medical community continues to unravel the complexities of peripheral neuropathy, testosterone enanthate stands as a beacon of potential therapeutic innovation.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Associated Risks in the US [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Long-Term Health Risks of Testosterone Enanthate Use in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Low Testosterone Treatment [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Sleep Quality in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Dispelling Myths and Understanding Facts for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Cognitive Function in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Prostate Risks, and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Cycle: Enhancing Performance and Managing Risks in Athletes [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Personalization, Monitoring, and Lifestyle Integration for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Blood Sugar Levels in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Withdrawal: Symptoms and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Male Fertility: Insights for American Patients [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Obesity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Ethical Dilemmas of Testosterone Enanthate Use Among American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Enhancing Veteran Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Effects on Hair Growth and Loss in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Appetite and Digestion in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential New Treatment for Allergies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Injury Recovery in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Joint Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Anemia in Hypogonadal American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Endurance in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Cultural Perceptions and Masculinity in American Society [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Combating Age-Related Decline in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Solution for Muscle Wasting in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Process, and Risks for Men Over 50 [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Stress Management Tool for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Skin Elasticity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Treatment for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Endurance in American Male Athletes - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Limitations, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat, Boosting Performance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: Risks and Recommendations [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Vision and Eye Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Costs, and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Dosage, Monitoring, and Lifestyle for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Impacts on Life Expectancy and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Post-Surgical Recovery in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Respiratory Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Autoimmune Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Role in Managing Diabetes in American Men: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Kidney Function Impact in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Hearing Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Liver Health in American Men: Risks and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Hypertension in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Male Reproductive Health and Fertility in America [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Treatment for Gastrointestinal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Neurological Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Adrenal Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle and Bone Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Thyroid Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Endocrine Impact in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Respiratory Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Males: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Emerging Role in Dermatology for American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Hematological Health in American Men: Benefits and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Metabolic Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Neurological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Metabolic Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: An Analysis [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Potential Benefits for Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Impacts and Management of Reproductive Health in Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Key Role in Treating Hypogonadism and Enhancing Male Health [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Potential Treatment for Hematological Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Gastrointestinal Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Neurological Impact on American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Effective Management of Low T in American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 640